Europe / Spain / 10/06/2020 / Author: Manuel Planelles / Source: english.elpais.com
Although levels remain below average, a spike in nitrogen dioxide has been detected as the country relaxes its confinement measures.
There has been a historic fall in air pollution as a result of the coronavirus crisis, just as there has been a historic global shutdown of economic activity. In Spain, pollution levels plummeted almost overnight when the government declared a state of alarm on March 14 and introduced strict confinement measures in a bid to curb the coronavirus outbreak.
In the first three weeks of the lockdown, the concentration of nitrogen dioxide – which is closely linked to car fumes – fell more than 50% in the air-monitoring stations across the country.
In the first week of June, the average concentration of nitrogen dioxide was 32% less than the average from the same period over the last four years.
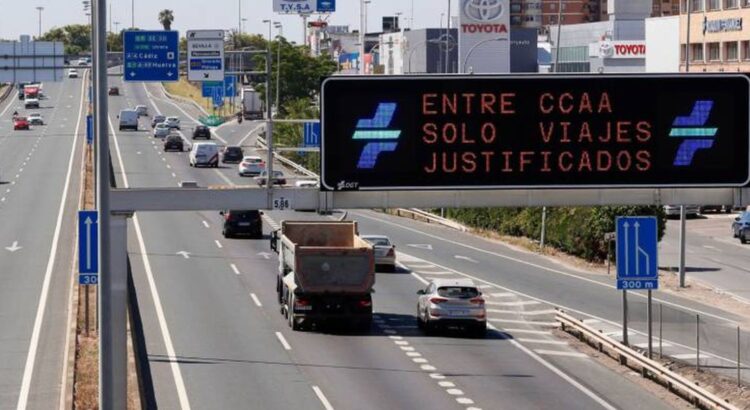
But as Spain began to deescalate the confinement measures, more traffic has returned to the roads, and nitrogen dioxide levels are once again on the rise. This increase was calculated by EL PAÍS based on the data from air-monitoring centers from the 15 most populous cities in Spain, which are home to more than 10.7 million people, or around one fourth of the total population.
Since the beginning of the coronavirus crisis, the European Environment Agency (EEA) has been compiling and sharing the weekly evolution of several pollutants as recorded by around 3,000 air-monitoring centers in the European Union. Thanks to the work of the EEA, it is possible to follow the changes in air-pollution levels during the crisis.
These changes are most apparent in the fluctuating levels of nitrogen dioxide, a harmful composite that can cause respiratory, circulatory and immunological problems. Given the pollutant is closely linked to traffic in cities, it is easy to see the connection between the fall in emissions and the coronavirus lockdown. But, as with all pollutants, meteorological conditions also affect its concentration. According to the EEA, air pollution causes 400,000 premature deaths in Spain every year.
During the first four weeks of confinement, there was a sudden drop in the level of nitrogen dioxide in Spain. Emissions of the pollutant fell to their lowest level in the week between April 6 and 12. The average concentration of nitrogen dioxide, as recorded in the 15 Spanish cities, plummeted nearly 65% compared to the average of the same week from the last four years (2016-2019). After that week, levels began to plateau, before rising again during May 11 and 17.
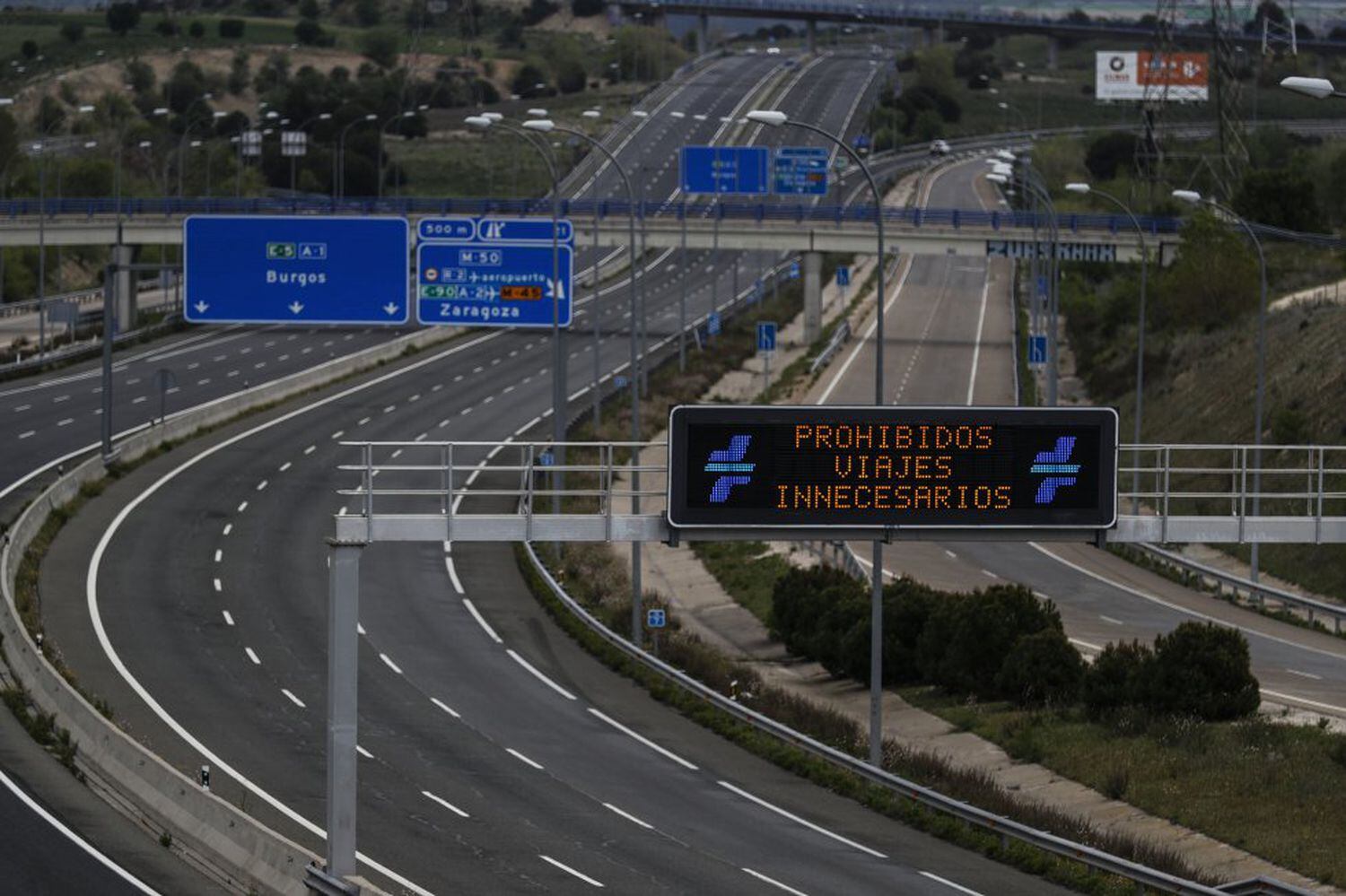

Despite this increase, the concentration of nitrogen dioxide in Spain remains well below average and far from what was recorded before the coronavirus lockdown was introduced. In the first week of June, with all of the country deescalating the confinement measures, the average concentration of the pollutant was 14.4 micrograms per cubic meter, based on the records from the 15 air-monitoring stations. This is 32% less than the average from the same period over the last four years.
Adrián Fernández, the head of mobility at Greenpeace Spain, explains that while the entire country began easing the lockdown measures on May 25, most schools and educational facilities remain closed and many employees continue to work remotely, meaning there has been less traffic on the roads.
“This crisis should not mean that measures against the most polluting forms of transportation are held back,” he warned.
Miguel Ángel Ceballo, an air-quality expert at the environment group Ecologists in Action, adds that the coronavirus crisis has also “stigmatized public transportation,” with many fearing contagion.
Financial aid for automobile sector
On May 31, Spanish Prime Minister Pedro Sánchez of the Socialist Party (PSOE) announced a plan to provide financial aid to the automobile sector. But according to Carlos Bravo, an expert in energy from the conservation association Salvia, this initiative could encourage the sale of gasoline and diesel cars.
Salvia, and other environmental groups including the Renewable Energy Foundation (FR), have come together to call for the “efficient and responsible use” of public funds and for the government plan to focus “primarily on boosting electromobility.” According to Bravo, “the true transformation will happen by supporting electric and hybrid cars, which are the ones that really reduce pollution and carbon dioxide emissions.”
The expert, who also expressed concern about the “uptick in the use of private vehicles” in Spain, said that Germany is leading the way with a multimillion-euro recovery plan that only includes direct aid for the purchases of electric cars. “If Spain wants to have a future in this industry, it must back electromobility,” explains Bravo.
When Sánchez announced the plan, he did not specify whether it would include aid to buy gasoline cars. But one top official in the Industry Ministry has said that the plan should be extended to these types of vehicles, as has been requested by the Spanish Association of Automobile and Truck Manufacturers (Anfac). Before the prime minister’s announcement, the Ecological Transition Ministry was finalizing the approval of a €65-million aid plan exclusively for electric cars.
Source and image: https://english.elpais.com/society/2020-06-09/spain-sees-rise-in-air-pollution-as-coronavirus-lockdown-eases.html
English version by Melissa Kitson.












 Users Today : 84
Users Today : 84 Total Users : 35402633
Total Users : 35402633 Views Today : 103
Views Today : 103 Total views : 3331723
Total views : 3331723