Asia/ Japan/ 27.05.2019/ Source: www.japantimes.co.jp.
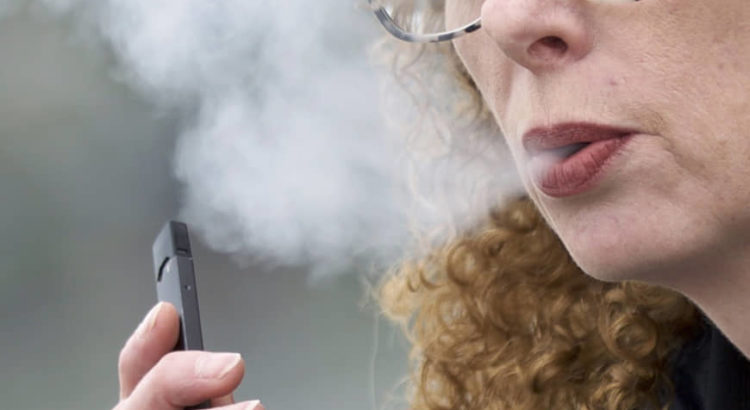
A glimpse of student athletes in peak physical condition vaping just moments after competing in a football game led Stamford High School Principal Raymond Manka to reconsider his approach to the epidemic.
His school traditionally has emphasized discipline for those caught with e-cigarettes. Punishments become increasingly severe with each offense, from in-school suspensions to out-of-school suspensions and, eventually, notification of law enforcement.
But Manka began thinking about it more as an addiction problem, and less of a behavior issue, after seeing the two players from another school vaping near their bus. “It broke my heart,” said Manka, whose school is now exploring how to offer cessation programs for students caught vaping or with vaping paraphernalia.
“We’ve got to figure out how we can help these kids wean away from bad habits that might hurt their body or their mind or otherwise create behaviors that can create habits that will be harmful for the remainder of their lives,” he said.
Schools elsewhere have been wrestling with how to balance discipline with prevention and treatment in their response to the soaring numbers of vaping students.
Using e-cigarettes, often called vaping, has now overtaken smoking traditional cigarettes in popularity among students, says the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Last year, one in five U.S. high school students reported vaping the previous month, according to a CDC survey .
E-cigarettes produce an aerosol by heating a liquid that usually contains high levels of nicotine — the addictive drug in regular cigarettes and other tobacco products — flavorings and other chemicals. Users inhale this aerosol into their lungs; when they exhale, bystanders often breathe it in too.
Compared with regular cigarettes, the research on the health effects of e-cigarettes is painfully thin. Experts say that although using e-cigarettes appears less harmful over the long run than smoking regular cigarettes, that doesn’t mean they’re safe — particularly for youth, young adults, pregnant women or adults who do not currently use tobacco products.
“Studies have shown that e-cigarette use among young people is potentially associated with an increased risk of progressing on to cigarette use and to vaping cannabis, which has become increasingly common in recent years,” said Dr. Renee Goodwin, a researcher and professor of epidemiology at the City University of New York and Columbia University who studies tobacco and cannabis use.
Besides nicotine, e-cigarettes can include other harmful substances, including heavy metals like lead and cancer-causing agents. The vaping liquid is often offered in a variety of flavors that appeal to youth and is packaged in a way that makes them attractive to children. And the long-term health effects, Goodwin noted, are unknown.
Experts say the CDC classifies e-cigarettes as a tobacco product, and many schools lump vaping in with tobacco use in applying codes of conduct, treating offenses similarly.
In Connecticut alone, administrators dealt with 2,160 incidents in which students were caught vaping or with vaping paraphernalia in violation of school policies during the 2017-18 school year, up from 349 two years earlier. The schools issued 1,465 in-school suspensions and 334 out-of-school suspensions, according to the state Education Department.
Nationwide, some schools have removed bathroom stall doors or placed monitors outside of restrooms to check students in and out. Others have installed humidity detectors that sound an alarm when vapor clouds are detected.
Lawmakers are beginning to show similar concerns. Oklahoma has passed legislation to ban vaping on school property, and a dozen states have passed legislation to increase the age for smoking and vaping to 21.
Nevertheless, some school districts have begun taking a more comprehensive approach by emphasizing treatment and prevention.
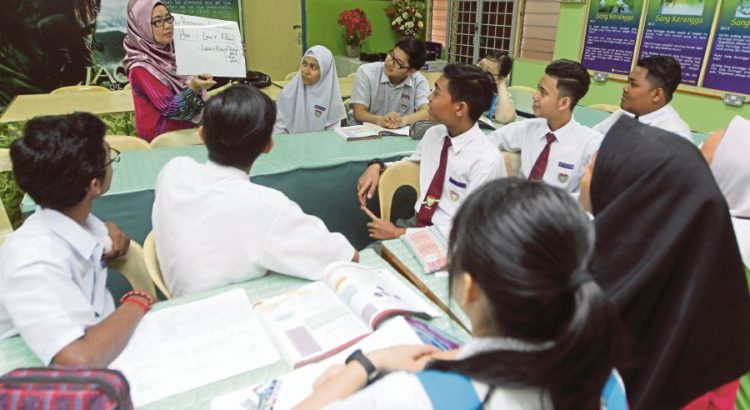
The Conejo Valley Unified School District in Southern California recently shifted from suspending students for a first offense to sending them to a four-hour Saturday class on the marketing and health dangers of vaping. A second offense results in a one-or-two-day suspension coupled with several weeks of a more intensive six-week counseling program that includes parents.
“I think we are seeing quite a bit of success, basing it on the reduction this year in both the number of incidents reported on campus and the number of suspensions,” said Luis Lichtl, the district’s assistant superintendent.
“The schools that seem to be most effective are those that are of course enforcing their disciplinary code — they can’t do otherwise — but are using that as the floor and not the ceiling,” said Bob Farrace, a spokesman for the National Association of Secondary School Principals.
Linda Richter, an expert on vaping and adolescent substance use who works at the New York-based Center on Addiction, suggests that schools provide information about the health consequences and how companies have manipulated students to use vaping products by making it appear fun and cool. She said that two-pronged approach led to a successful decrease in the use of traditional cigarettes.
“To expect a 13-, 14- or 15-year-old to break an addiction by yelling at them or suspending them, it’s just not going to happen,” she said. “They need help, treatment, counseling, support, education and understanding.”
Dr. J. Craig Allen, medical director at Rushford, a mental health treatment center in Meriden, said suspending teens for vaping may be counterproductive.
“If your solution is to send these kids home, what do you think they are going to be doing at home,” he said. “They are going to be taking rips off their Juul all day long to kill the time.”
Thomas Aberli, the principal at Atherton High School in Louisville, Kentucky, said it began an intensive anti-vaping education program this year with the help of the American Association of Pediatrics. Teaching teens about how vaping companies have been courting them with flavored products seems to be having an effect.
“You could tell how angry they were getting with this sense of manipulation,” he said. “That was really a turning point for us in knowing the best way to approach this problem.”
Other schools have continued to emphasize discipline in crackdowns on teen vaping.
At the Mattawan Consolidated School District just outside of Kalamazoo, Michigan, Principal Tim Eastman recently wrote to parents that students found congregating in bathrooms or parking lots will be taken to the office and searched.
“Anyone found with vaping equipment will face suspensions,” Eastman wrote. “Although this may seem extreme, the health and safety of our students is too important to ignore.”
Eastman said the school is not currently providing those caught vaping with any additional education or medical intervention, but is considering it.
Source of the notice: https://www.japantimes.co.jp/news/2019/05/27/world/science-health-world/discipline-treatment-schools-rethinking-vaping-response/#.XOutY9IzbMw







 Users Today : 44
Users Today : 44 Total Users : 35460253
Total Users : 35460253 Views Today : 59
Views Today : 59 Total views : 3418954
Total views : 3418954