By the co-Leads of the thematic Action Track on teachers, teaching and the teaching profession, representatives of Nigeria, Romania and the International Task Force on Teachers for Education 2030
Ahead of the Transforming Education Summit in September, education ministers along with hundreds of youth, teachers and other stakeholders are meeting this week in Paris to revitalize efforts to achieve Sustainable Development Goal 4 and transform education. Together, they are considering how to deliver on existing commitments and identifying new ways to recover pandemic-related learning losses and transform our education systems for sustainable futures. To help the education community get back on track and give new life to efforts to achieve SDG 4 between now and 2030, today we are launching a campaign to put teachers, teaching and the teaching profession at the heart of education transformation.
Barriers to the teaching profession are barriers to quality education
Putting qualified and motivated teachers into classrooms is the single most important thing we can do to support better learning outcomes. In many parts of the world, teachers are too few, classrooms are too crowded, and teachers are overworked, demotivated and unsupported, with the result that learning outcomes suffer. Alongside the educational disruption of the COVID-19 pandemic, the quantitative and qualitative “teacher gap” is throwing our education targets, including SDG 4, way off track. Children in remote or poor areas are disproportionately affected.
More teachers are desperately needed. Globally, we are still millions of teachers short: recent estimates point to sub-Saharan Africa alone needing 15 million teachers to achieve SDG 4 by 2030. Compounding the teacher shortage, in many countries, teachers lack minimum qualifications and training.
Even if teachers are qualified, teacher retention rates are often low since poor working conditions and lack of support drive teachers to change careers. Too often, becoming a teacher is not seen as an attractive career path because the profession is poorly paid and poorly regarded. In many countries, teachers are simply not being paid a living wage, further undermining education systems.
The use of digital technology in education holds much promise for opening up learning to more children and young people. However, we need to improve access to technology for both teachers and learners, especially in sub-Saharan Africa and low-income countries where on average less than 1 in 3 schools have computers for learning and fewer than 1 in 5 have internet. We also need to better prepare teachers to adapt their teaching so that ICTs are used as a means to an end, not as an end in itself.
#TeachersTransform learning
During the COVID-19 pandemic, teachers were resourceful in continuing to educate and innovate in difficult circumstances. They forged new ways of teaching and engaging their students. Importantly, they supported students beyond academic learning, contributing to their well-being. In Rwanda, teachers innovated by using play-based learning to help rebuild students’ well-being following school closures and lockdowns. In Uganda, teachers used the radio to address learning gaps and to provide professional and well-being support to remote teachers affected by isolation.
Teachers know how to achieve the best learning outcomes for their classrooms and they should be given autonomy to organize and adapt to the changing needs of their students. This kind of flexibility has the potential to foster both bottom-up (grassroots) and top-down (system-wide) transformations. To support such efforts, school leaders should be given more autonomy and responsibility. And particular attention must be given to teachers working with displaced and refugee populations and those affected by conflict, including the educators themselves.
Governments and civil society must work together to build respect and trust for teachers and appreciation for the role teachers play in educating future generations. Serious commitment and investment are needed to grow the teacher workforce, improve training and support, include teachers in decision-making and raise the profession’s status.
Education systems need to transform to better support the teaching profession
To genuinely transform education, we must build a workforce of teachers who are engaged, respected and properly resourced. Consultations held as part of the thematic Action Track on teachers, teaching and the teaching profession have suggested three ways in which we can achieve this goal.
First, comprehensive national policies for the teaching profession need to be developed. These policies must provide stronger scaffolding for teacher preparation, career paths and governance, and should also lay out ways to empower leadership and promote innovation, develop qualitative frameworks and provide better work conditions.
Secondly, we need teacher participation in every step of decision-making and policy-making, through robust social dialogue. Teachers were at the forefront of the education response to COVID-19 and are best placed to address learning gaps and long-term learning solutions in the pandemic’s aftermath.
And lastly, we need to increase investment in wages, professional development and working conditions. As part of this, governments must honour their commitment of 20% annual expenditure on education. Domestic education budgets must grow and international donors need to increase levels of education aid to meet the benchmark of 0.7% of gross national income. Teacher policies should be properly costed and effectively implemented, especially in countries with the most severe shortages.
Much work remains to be done, but one thing is clear: teachers are central to transforming education and alleviating the global education crisis. Only together can we reimagine education and deliver on the promise of quality education for all.
Join the #TeachersTransform campaign launched today by the International Task Force on Teachers for Education 2030, as part of the thematic Action Track on teachers, teaching and the teaching profession. More information here.
The post To transform education, we need qualified, motivated and supported teachers appeared first on World Education Blog.

 for an education, and 222 Million Dreams
for an education, and 222 Million Dreams
 to use that education to make the world a better one than the world in which they suffer today
to use that education to make the world a better one than the world in which they suffer today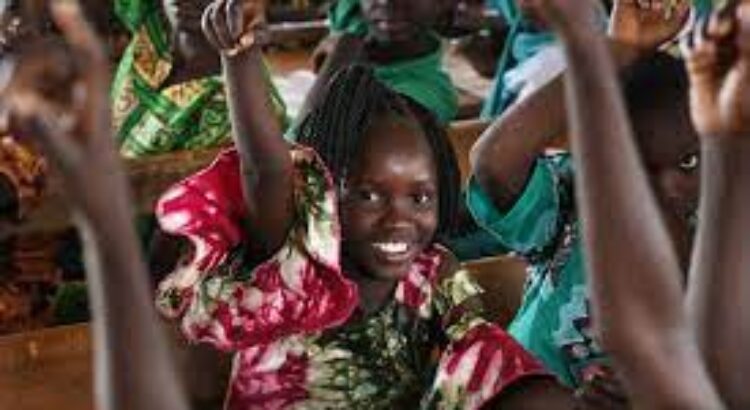







 Users Today : 174
Users Today : 174 Total Users : 35459769
Total Users : 35459769 Views Today : 331
Views Today : 331 Total views : 3418303
Total views : 3418303