By Michael Hoffman.
What’s wrong with the following story?
A magician, skilled but unlucky, finds success passing him by. One day, wandering lost in gloomy thoughts, he meets a boy who is unhappier still. The magician does some tricks. The boy cheers up. They become friends. They agree to meet the next day.
That evening the magician receives a visit from a friend. The friend brings news: The scheduled performer at the next day’s magic show can’t make it. Will the magician fill in?
Here it is, at last, the big break! Ah, but — the boy! He has promised to meet the boy! Can he disappoint him? No, he cannot. Success, fame, fortune are important, but friendship is more so. He will turn down the offer. He will keep his promise.
What’s wrong with the story? As a fairy tale, nothing. But as a moral lesson — since that’s what it’s meant to be — it seems to lack an essential ingredient: realism. Does real life work that way? Can it? Should it? If Japan’s did, what would become of its economic competitiveness?
It’s an old story, going back some 40 years, according to the Asahi Shimbun, and it has found its way, in one form or another, into all eight of the government-approved textbooks in use in a new — resurrected, rather — elementary school subject known as moral education. Discredited following World War II for its prewar and wartime militarist leanings, moral education sank into an informal limbo from which a reform backed by the education ministry has rescued it, effective this year in elementary schools, next in junior high schools.
History aside, critics fret about a key element of the reform. Moral education is now, as it was not in its informal phase, to be graded. How can teachers grade morality? By rewarding the loudest professions of determination to emulate the magician? Hypocrisy pays, while sincerity must be its own reward.
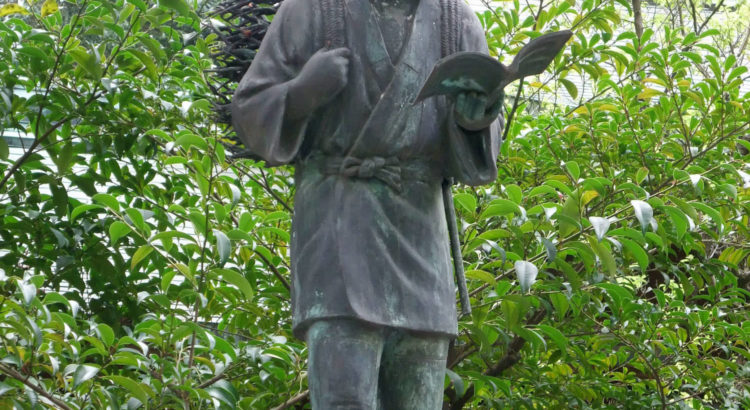
Another character figuring prominently in the new moral education textbooks is one Ninomiya Kinjiro (1787-1856). Born to a peasant family in Sagami Province (today’s Kanagawa Prefecture), he taught himself to read, worked himself up from poverty and became a noted figure of his time — an agronomist, economist, philosopher and forceful advocate for the starving poor. His posthumous life extended deep into the 20th century, via a famous 1-meter-high statue, much reproduced and adorning elementary school grounds across the nation, instantly recognizable by the load of firewood on the boy’s back and the book in his hand, symbolizing his indefatigable determination to work and better himself at all costs.
Readers of Kappa Senoh’s fictionalized wartime memoir “Shonen H” (“A Boy Called H”) will remember H, as an elementary school fourth-grader, getting into trouble over Ninomiya Kinjiro. A teacher rebukes H for reading while walking. “But,” protests H, “Miss Hayase (his homeroom teacher) said we should model ourselves on the statue of Ninomiya Kinjiro.” Yes, says the teacher, but not to extremes: “Modeling yourself on him means you should study hard, not that you should read as you walk.”
During the war the statues were melted down for ammunition, and Kinjiro more or less disappeared from view. He’s back — raising, on his return, the same question raised by the fictional magician: Is morality realistic?
Yasuhiro Ninomiya, a 71-year-old descendant of Kinjiro’s and a member of the Association of Japanese Intellectual History, tells the Asahi Shimbun that legend somewhat exaggerated his ancestor’s merits, considerable though they were. Kinjiro did teach himself to read, says Yasuhiro — but later in life, not as a child. And a famous story of him — again as a child — making straw sandals on his own initiative for laborers building a levee is “probably baseless” — a late 19th-century authoritarian government’s conscious attempt, in Yasuhiro’s view, to symbolize selfless dedication in opposition to a campaign then simmering for individual rights.
Two textbooks feature that story. Does factual accuracy matter? Yes, but secondarily, an education ministry official tells the Asahi Shimbun: “The essential point, in selecting content, is its educational value. Factual accuracy may or may not be an obstacle in that regard.”
Suppose a bright kid raises his or her hand in class and asks, “Is this story true?” What would the teacher say in reply — that “factual accuracy may or may not” matter?
It seems to matter less and less in society as a whole. Two examples, one benign, the other not:
Earlier this month the business magazine President ran a feature on job interviews. How should a job candidate approach one? Gingerly and yet boldly — gingerly because so much depends on it, boldly because bold is what an employer wants its employees to be. President cites an astonishing fact: A first impression of a stranger we meet is formed within, on average, 0.2 seconds. Once formed, it is more or less indelible. (“If you spill red ink on white paper, you can’t change it to blue ink,” is how psychologist Isamu Saito puts it.) The successful job candidate is he or she who seizes control of that crucial one-fifth of a second.
There are ways to do it. Sixty percent of a first impression is determined by the expression on your face. What do you want yours to say? Compose it so that it says it. Dress, too, says Saito, is important. The cut and colors of your suit, necktie and accessories send subliminal messages: red — extroverted and novelty-seeking; blue — polite, knowledgeable and traditional; gray — unassertive; and so on. What do you want to convey to your prospective employer? Whatever it wants to see in you — which you’ll know, having done the requisite preliminary research into the company’s corporate character.
Sincerity? A virtue no doubt, but first things first, and the first thing is: Get that job!
Having got it, the “first thing” is apt to become: sell products, maximize profits, gain power, keep power, expand power, protect your boss, protect yourself — and so on. The long list of corporate and government scandals unfolding over the past year and a half suggests a moral crisis that is pervasive rather than aberrational.
Truth? The admission this month by KYB Corp., a manufacturer of earthquake shock absorbers, that it has been fabricating safety data for more than a decade, is merely the latest reminder among many that, in a society whose primary goals are not moral but economic, the moral high road belongs exclusively to itinerant, luckless magicians. More power to them.
Source of the article: https://www.japantimes.co.jp/news/2018/10/27/national/media-national/moral-education-may-not-reflect-realities-life-japan/#.W95XW9ThDwd






 Users Today : 4
Users Today : 4 Total Users : 35459910
Total Users : 35459910 Views Today : 4
Views Today : 4 Total views : 3418469
Total views : 3418469