By: Kevin McKenna.
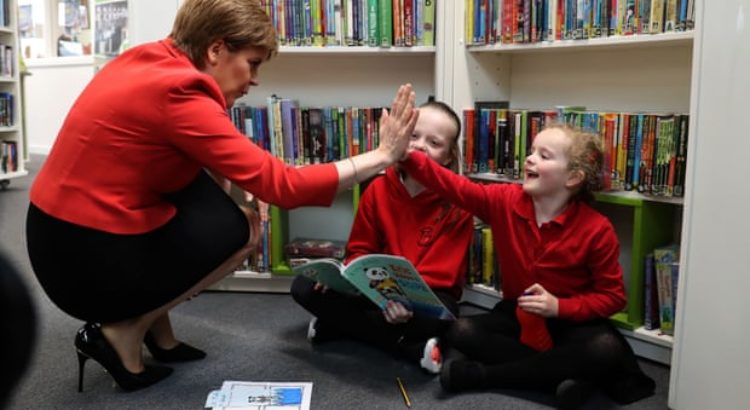
The first minister has praised the contribution of Catholic schools to ‘modern Scotland’
There was a time not very long ago – perhaps 25 years, maybe 30 – when Scotland wasn’t obsessed with how its education system was delivered.
This is not to suggest that education was ever deemed less than crucial to the nation’s future. It’s just that, until recently, you never had the sense that education on its own could destabilise governments. There was a received wisdom that Scotland possessed the finest education system in the world. This probably resonated for many years after it ceased to be true.
The intensity we now bring to any debate on the subject was also largely absent. The optimism inspired by Anthony Crosland’s expansion of the comprehensive education system in 1965 cannot be overstated. For tens of thousands of UK families, these stretched horizons and parted clouds. They held out the genuine prospect of “bettering” yourself. The vast deposits of emotional trust that working-class people invested in Harold Wilson’s Labour government as a result cannot be overstated.
This was an era when working-class people were still content to rent their homes from the local authority and the concept of home ownership – moving on, up and beyond the environs of your birthplace – was unknown. The idea of living in an area with a “good school” was also exotic. You simply took the school you were given; we all knew who the bright children were and who would start every day two goals down. The nature and quality of a school couldn’t change that.
In Scotland, as in the rest of the UK, remorseless free market capitalism began to undermine the concept of comprehensive education. Schools once considered to be excellent were soon deemed to be “rough”, as “aspirational” families moved from their traditional heartlands. The schools where they began to settle quickly had “desirable” status conferred upon them. As newspapers began to publish league tables of academic attainment, house prices rose and education became the main topic of conversation where the expanded middle classes gathered. To be caught short at the school gates on the details of the Herald’s academic league tables was to risk becoming a social pariah.
There was an increase in expectations of families who had once simply been grateful that the 11-plus system had been replaced with the much fairer comprehensive one. The concomitant pressure on successive Scottish governments to meet these heightened expectations has become almost unbearable. Initiatives have tumbled forth: Higher Still, Curriculum for Excellence and still the attainment gap between the disadvantaged and the affluent remains.

Scottish Conservatives relish those times of the year when measures of attainment are published. They never consider the effects of punitive austerity in neighbourhoods left devastated by it. How does a child concentrate on his studies when he doesn’t know what will confront him when he gets home? When the question is not: “What’s for dinner?” but: “Will there be dinner?”, double maths takes a back seat.
Yet, Nicola Sturgeon has publicly – and repeatedly – staked her career on narrowing the gap. Some developments in the last few weeks have relieved the pressure on her. Scotland’s two greatest universities, Glasgow and Edinburgh, announced that their widening access programmes for children from disadvantaged communities have begun to bear rich fruit. In particular, the medical school at Glasgow University has overseen an astonishing increase in the number of poorer students accessing medicine, one of the most coveted and elite courses in the UK. Painstakingly constructed over 10 years, the initiatives that have delivered this success are also beginning to trickle down through entire year groups in schools within the target lowest 20% of MD (multiple deprivation) communities.
The first minister has also had cause to acknowledge another much older and well-established success story. Last week was the centenary of the passing of the 1918 Education (Scotland) Act, which paved the way for state-funded Catholic schools. In a speech this year, Sturgeon went further than any previous first minister in acknowledging and endorsing the hugely significant contribution Catholic schools have made to Scottish society.
As she unveiled an extra £100,000 of funding for Catholic teacher training, she said: “Catholic schools have made a tremendous contribution to Scottish education and this is something we want to see continue. We value the contribution that Catholic schools make to modern Scotland.” She is aware of the extraordinary academic results achieved by Catholic schools in deprived areas. If the educational attainment gap is to narrow then Catholic schools will be a key factor. She knows it and so does her government.
Of course, in enlightened, progressive and modern Scotland, you can still hear liberal voices, usually on phone-in shows on BBC Radio Scotland, offering opposition to these schools. Some have recently come from the scarecrow wing of the SNP’s Westminster group. Their manufactured tolerance comes with strings attached regarding some of the teachings of the Catholic church.
This is when they pretend to be concerned with “bigotry” and “sectarianism”. If they did, they might wonder why Catholics in Scotland are more likely to be the victims of hate crime than all other faiths combined. Must be those wretched Catholic schools encouraging their pupils to be Catholic and upsetting people.
Source of the article: https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2018/nov/25/catholic-schools-improve-lot-poor-children






 Users Today : 71
Users Today : 71 Total Users : 35459977
Total Users : 35459977 Views Today : 95
Views Today : 95 Total views : 3418560
Total views : 3418560