By Mujib Mashal and Najim Rahim
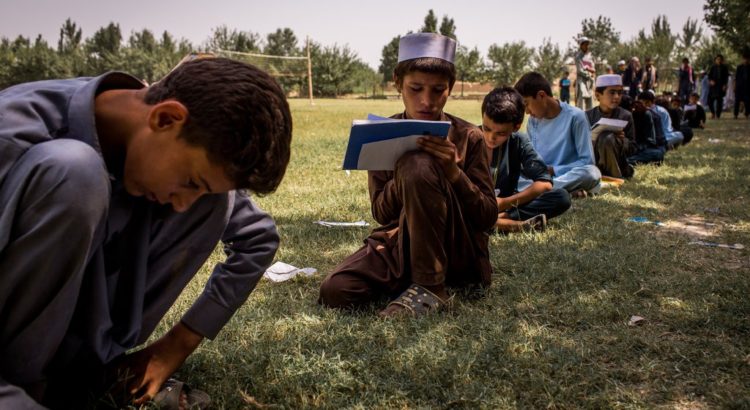
Before the start of another Afghan school year, about 200 tribal elders in the southeastern district of Laja Mangal gathered in a schoolyard for an important declaration: Any family that did not send its children to school would be fined $70, about half a civil servant’s monthly salary.
The district of about 50,000 people had built seven schools over the past 15 years, yet it had struggled to attract students from the mountainous area where the Taliban also have influence. The elders, feeling old tribal customs were holding back their children, thought the drastic measure was necessary.
“They see those people who go to school and become important people in the government and international organizations, so they have tasted the value of education,” said Khayesta Khan Ahadi, who was the headmaster of the first school built in the district.
Mr. Ahadi said local Taliban, after outreach by the tribal elders, announced their support for the decision from the loudspeakers of local mosques.
The tribal elders’ decision has gained attention across Afghanistan not just because it could help more children get an education, but also because it comes at a time when many remain deprived. Violence and corruption have overshadowed what was once a remarkable success story.
3.5 million children are unschooled.
That 3.5 million figure is according to Unicef. Seventy-five percent of them are girls.
The reasons vary. Violence remains high and widespread. There are too few female teachers, and many families will only let girls be taught by women. For many, going to school means a walk of many miles each day.
In certain parts of the country enjoying relative peace, however, female enrollment seems higher than that of boys.
In the central Bamian Province, 58 percent of the 162,000 students are female, according to Ayyub Arvin, the provincial director of education.
1,075 schools remain closed.
The country’s Education Ministry says it has 17,500 schools across the country, but 1,075 remained shut last year, largely because of raging violence. The south of the country, where violence has been relentless over the past decade, has been disproportionately affected by the school closures.
Activists say the number of closed schools is even higher. Mattiullah Wesa, who leads the organization the Pen Path, said they have counted 1,600 shuttered schools.
Of Afghanistan’s approximately 400 school districts, there are 48 districts where not a single male student has graduated from high school in the past 17 years, Mr. Wesa said. There are around 130 districts from where not a single girl has graduated from high school in the same period, he added.
Nearly half of schools lack buildings.
A survey of 32 of the country’s 34 provinces by The New York Times shows close to half the schools lack buildings. Provincial officials in these areas reported that more than 7,000 schools either teach in open air or have worked out temporary arrangements for classes in rental homes.
The provinces of Ghor and Herat in the west, Badakhshan in the northeast, and Nangarhar in the east had the highest number of schools without buildings, each with at least 400.
“Even inside the city, and the centers of the districts, we have schools that lack buildings,” said Rohullah Mohaqeq, the provincial director of education in Badakhshan.
Corruption hits every level.
Despite huge donor investment in Afghan education, corruption remains one of the major causes for its abysmal infrastructure.
The country’s education system is marred by corruption — from the smallest procedures of modifying school certificates, to the appointment of teachers and the handling of school construction contracts — a damningreport by the country’s independent corruption monitor said last year. People seeking a teaching job could pay as much as a $1,000 in bribes, nearly five months’ salary, to secure a position.
Recently, the government has tried to tackle corruption in the hiring of teachers by introducing a more rigorous process through its civil service commission. The Education Ministry is the country’s largest civil service employer.
Corruption has also been seen as a major reason for discrepancies in enrollment numbers. The country’s previous government had claimed more than 11 million children were in school, with allotted resources often going into the pockets of local and central officials. But the new government has placed that number anywhere between 6.2 million to a little over 9 million.
Pressure on Taliban works, sometimes.
Across the country, as violence has become the daily reality, elders have tried to figure out local arrangements that would reopen schools.
“The good news is that the Taliban now want schools in their area of control because of local pressure,” said Dawood Shah Safari, the head of the education department in Helmand, whereas many as 30 school buildings are used as cover by fighters on both sides. “Villagers keep coming to me with letters of approval from the Taliban, asking us to open schools.”
In northeastern Warduj district, which is largely controlled by the Taliban, officials said 16 schools that had been closed for two years were reopening this spring after talks with the group.
The 13 schools in the Nawa district of Ghazni Province have been closed since 2001, with no child able to attend, according to Mujib-ur-Rahman Ansar, the provincial director of education. But recently, local elders convinced the Taliban to allow the schools to reopen. As many as 25,000 children could attend if the Taliban allow both boys and girls, Mr. Ansar said.
“I must tell you that there isn’t any professional teacher for these students,” Mr. Ansar said. “I will hire one to two teachers, and the guy may only be able to read and write, with a ninth or 10th grade education, not much more.”
Other times, Taliban still threaten.
Last week, as schools prepared to open in the northern province of Kunduz, the official ceremony in the capital city had to be shifted because of Taliban threats.
Only a quarter of Kunduz city’s 130 schools have opened their doors to students. The rest, even those under nominal government control, are waiting for the Taliban to give the green light.
The dispute seems to be over the mechanism of paying the teachers. The Taliban say they are not opposed to education but will keep the schools shut until the government changes the method of paying teachers from bank deposits to cash.
On Saturday, hundreds of teachers marched in Kunduz city, saying they hadn’t been paid for five months.
Mawlawi Bismillah, the Taliban’s head of education for Kunduz, said the group’s position was intended to reduce the headache for teachers, who need to make long trips to the provincial capital to withdraw their money. It’s easier if the money is delivered by middlemen, he said.
Government officials say the Taliban are pushing the change because they want a cut.
“They should come and monitor the payment process,” Mr. Bismillah said. “In our areas of control, we have very active attention and monitoring.”
Source of the article: https://www.nytimes.com/2018/04/01/world/asia/afghanistan-schools-taliban.html






 Users Today : 215
Users Today : 215 Total Users : 35459810
Total Users : 35459810 Views Today : 377
Views Today : 377 Total views : 3418349
Total views : 3418349