By: Pablo Vivanco
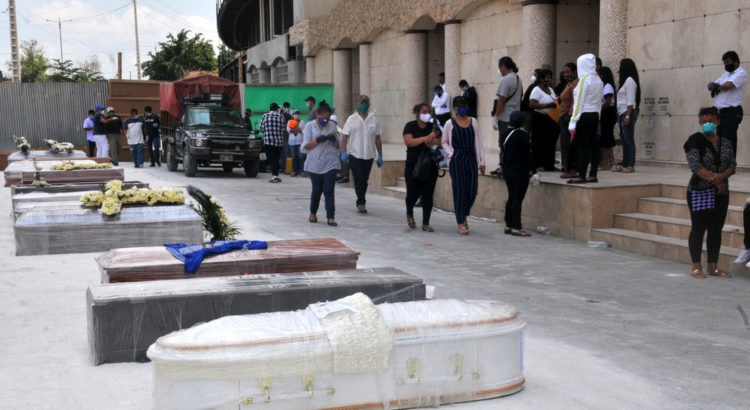
Even by Latin American standards, the images emerging from Ecuador’s largest city, Guayaquil, have been shocking. Since the first case of Covid-19 was announced in late February, Ecuador has turned into the epicenter of the crisis in Latin America, touching many of the city’s 3 million residents.
“I know several people who have been infected and also some who have died,” Guayaquil resident Xavier Flores Aguirre tells me. “I think that by this point, everyone in Guayaquil is experiencing something similar.”
In the last weeks, videos and photos have been circulating on social media showing wrapped and covered bodies strewn on the streets in 30 degree temperatures.
Lenín Moreno
✔@Lenin
Colegas presidentes, no nos hagamos eco de las noticias falsas que tienen clara intencionalidad política. ¡Todos estamos haciendo esfuerzos en la lucha contra el #Covid19! La humanidad nos necesita unidos.
Government officials initially played down reports about the outbreak in the city, and Ecuadorian president Lenin Moreno even tweeted on April 1 that this was “fake news with clear political intent.”
Ecuadorian authorities have become accustomed to either denying inconvenient facts, or to simply blame the previous government for any of the country’s woes, but when the mainstream media outlets that have towed government lines in the past began to report on the situation, they had no choice but to acknowledge what was happening.
#Ecuador ‘s reality in one picture, people are trying to find some dignity for their dead relatives in the middle of utter chaos and government’s indifference. We need international help. #SOSEcuadorNOW #COVID2019
But who is to blame for the post-apocalyptic scenes in Ecuador’s busiest port?
“I think that the fact that Guayaquil is the most affected population is related to the development model imposed by the political right in the city since the 1990s,” says Flores Aguirre.
Home to the country’s wealthiest people, Guayaquil has long been governed by the Social Christian Party, which has concentrated resources and efforts on supporting the export industries of the city. Social investments have historically been paltry, and in 2018 the city put aside more money for publicity than it did for health. Despite its ‘law and order’ mantra, Guayaquil retains the highest homicide rates, and it has also been deemed as a central gateway for cocaine to Europe.
But the lack of social infrastructure created under decades of uninterrupted rule in Guayaquil can only partly explain why the city accounts for some 90% of the confirmed Covid-19 cases in the country.
Since the beginning of the outbreak, the city’s leaders have carried on as usual, allowing large gatherings to continue and even encouraging people to flock to the Copa Libertadores match in the city. Over 20,000 people showed up to see Barcelona SC play Independiente del Valle in what is certainly a repeat of ‘biological bomb’ in the Champions League match in Northern Italy between Atalanta and Valencia.
Even as the city garners world wide attention for the disaster on the streets, Mayor Cynthia Viteri branded a ‘donation of 1000 cardboard coffins’ to the victim’s families as an act of ‘solidarity.’ The level of contempt and disregard that Guayaquil’s leaders have shown their residents is truly astounding.
But Viteri and her party share responsibility with their allies for this debacle.
“The highest authorities of the central government must be held responsible for the ineffective, late and reactive response,” says Flores Aguirre, who is a constitutional lawyer by trade.
As soon as he was elected, President Moreno back-stabbed his former left-wing allies, as well as predecessor Rafael Correa, by pacting with right-wing parties and groups to dismantle the institutions and policies created by the ‘Citizen’s Revolution’ that he helped usher in. He also cosied up to Washington and brokered deals with the International Monetary Fund, all the while pushing through harsh austerity measures that have gutted key social services and diminished the state’s capacity to respond to a crisis like this.
In the health sector, the Moreno government slashed spending from $306 million in 2017 to $201 million in 2018, and then $110 million in 2019, according to a March report from the Central University of Ecuador.
Just two weeks after the first confirmed Covid-19 case, Moreno announced another budget cut of $1.4 billion, including the elimination of 4 regulatory and control agencies, 3 public companies and 4 technical secretariats. Later in March, Ecuador chose to pay $324 million to creditors instead of making investments to stem the impact of the impending crisis.
This is no coincidence of course, as creditors such as the IMF make reduction of public spending a condition of their loans, and this was certainly the case for Ecuador, where the proposed cuts sparked weeks of violent protests in October of 2019.
Moreno worked to dismantle the apparatus and regulations created under Correa, in order to return the country towards the model of governance that his allies have been carrying out in Guayaquil for decades. Simply put, the tragedy unfolding in Guayaquil is the result of the political leaders being unwilling to seriously confront any sort of social crisis, let alone a health related one, and decimated institutions being unable to.
What’s more, the specter of the Guayaquil problem threatens to spread across the country, as the state struggles to ensure police are allowed to patrol the popular tourist city of Banos, or even to properly equip or pay doctors at public hospitals while they attend to the worst crisis that has hit the country since the devastating 2016 earthquake.
Comparing the response now with that of the Correa government in 2016, where the central government moved to coordinate relief and rescue efforts quickly, underscores the fact that what is playing out in Guayaquil is a man-made tragedy.
The government now acknowledges almost 4,000 cases and under 200 deaths, but surely this number is considerably higher. A joint military-police operation in the city has now begun picking up more than 100 bodies a day, and the country’s health minister said in an interview that as many as 1500 had died in the city so far.
Ecuador was already turning into a powder keg, as the October protest showed. However, this callous indifference in the handling of this crisis should make it clear that, to the country’s political elites, ordinary Ecuadorians are disposable. Once the dust has settled, those who have already had to scramble to dispose of the corpse of their uncle or grandmother won’t be likely to forget that quickly…
Source and Image: https://www.rt.com/op-ed/485211-ecuador-covid19-catastrophe-disposables/











 Users Today : 62
Users Today : 62 Total Users : 35459657
Total Users : 35459657 Views Today : 130
Views Today : 130 Total views : 3418102
Total views : 3418102