Africa/ South Africa/ 07.01.2018/By: Natasha Robinson/ Source: www.thesouthafrican.com.
What will it take to improve teacher quality and professionalism in the country?
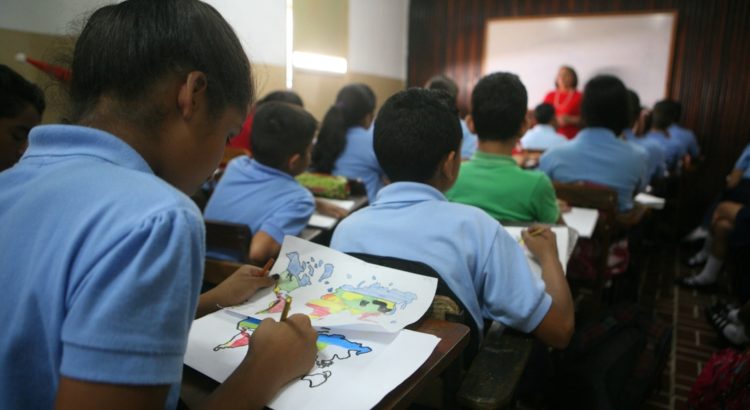
Half of all South African pupils who attended school for five years can’t do basic calculations. This is according to a 2015 TIMMS report on mathematics achievements among Grade 5 learners in South Africa.
At the same time, it’s calculated that 10% of the country’s teachers are absent from school each day, while researchfound that 79% of South African Grade 6 mathematics teachers were classified as having content knowledge levels below the level at which they were teaching.
Given that teacher quality is one of the biggest factors determining the learning outcomes of students, what will it take to improve teacher quality and professionalism in the country?
Numerous suggestions have been floated. But one idea has recently generated particular interest among education departments, statutory bodies, and academia – the introduction of “teacher professional standards”. These can be broadly defined as a set of common standards that include the professional knowledge, skills and conduct that characterise good teaching.
Their development began in the US in the late 1980s. It was stimulated by the view that higher expectations for student learning could be accomplished only by higher expectations of teaching quality. In the South African context, teacher standards are a response to a lack of teacher accountability. This has been identified as a cause of the poor quality of South African education.
The basic premise of teacher standards is that if you expect more from teachers, don’t allow them into the classroom until they’ve met a basic set of criteria, and hold them to account if they fall short, then the quality of teachers will improve.
But introducing teacher standards in South Africa also comes with a caveat. Research into the value of teacher standards for South Africa warns that this approach could serve to de-professionalise the country’s teaching force if not approached carefully.
This is because there are effectively two types of teacher standards, and it’s important not to conflate the two. There are standards that professionalise teaching and standards that simply manage teachers. While standards which professionalise create cultures of collegiality, expertise and pride among teachers, standards that manage can leave them feeling brow-beaten, untrusted, and demotivated.
Yet management standards are often mistaken for professional standards. When this happens, teacher morale drops. This is a common trend in countries like South Africa which have a “vicious” rather than “virtuous” schooling cycle.
How the schooling cycle works
The quality of a nation’s teachers cannot be divorced from the quality of its learners exiting schools. This is because successive cohorts of learners progress through school, enter university as student teachers, and graduate as teachers where they nurture the next cohort through the cycle. The end of school is therefore the beginning of higher education.
In a virtuous schooling cycle, such as Finland, education is a desirable career choice for top graduates. This allows for competitive entry requirements for teacher education programmes, which in turn allows for rigorous and challenging courses. This, in turn, produces high quality teachers who improve learner outcomes. The quality and professionalism of the teachers nurtures the next generation of high-quality teacher trainees.
In a virtuous cycle the system can afford to set standards that reflect the best professional knowledge internationally. Initial teacher education is intensive and teachers exit the programmes with high levels of subject and pedagogical knowledge. As a result, their learners perform well and the school system enjoys a high level of public esteem.
Consequently teaching is a prestigious and attractive profession which recruits the brightest and most motivated school graduates, who don’t require continual monitoring and oversight. Teachers instead enjoy professional autonomy; they are trusted in key decisions about their teaching and professional development.
Compare this to South Africa, which has a vicious schooling cycle. Initial teacher education is highly variable but generally insufficient. For example, a study found that three out of five of the Higher Education Institutions that were sampled provided no English language, literature, or linguistic education for teacher trainees not specialising in this subject, despite poor English language proficiency among teacher trainees being a ubiquitous concern.
Unsurprisingly then, research on newly qualified teachers indicates that students enter their studies with very poor skills, and leave with little more. Consequently, their learners do very poorly and teaching is perceived as a low status career. Teacher education programmes are therefore in general unable to reliably attract high quality graduates, and so tend to be less demanding. The vicious cycle repeats itself.
In vicious schooling cycles governments take it upon themselves to hold teachers accountable. Standards are used to manage teachers, and to protect students from the worst educators through supervisory surveillance and control. Invariably, the relationship between teacher unions and governments becomes antagonistic and generates feelings of fear and mistrust. This, in turn, alienates the best school graduates who frankly have better career options.
While in-service training programmes attempt to make up the backlog, and some are succeeding in achieving small learning gains, they cannot fully compensate for the lack of teacher skills resulting from poor initial teacher education and generally unskilled matriculants.
Not all standards professionalise teaching
Given its vicious cycle, management standards may be more likely than professional standards in South Africa. Does this mean that South African teachers are damned to the stick, rather than the carrot? Not necessarily. There are many excellent teachers who are hungry for opportunities to develop in ways that nurture autonomy and collegiality.
South Africa should not shy away from developing and promoting professional best practice, and providing the opportunities for teachers to reach them.
At the same time, management standards must be considered carefully. While they may prevent the worst teaching, they’re unlikely to create the professional culture that promotes the best teaching and attracts the best candidates.
Source of the notice: https://www.thesouthafrican.com/south-africa-school-teacher-crisis/











 Users Today : 32
Users Today : 32 Total Users : 35474743
Total Users : 35474743 Views Today : 43
Views Today : 43 Total views : 3574786
Total views : 3574786