Dr. Henry Giroux
Thousands of teachers and students are walking out of schools, marching in the streets, and raising their hands and signs in protest against the war on education. Most recently, South Carolina has joined the wave of teachers’ protests and strikes taking place across the nation. In the age of illiberal democracy and the growing fascism of the Trump administration, the unimaginable has once again become imaginable as teachers inspired and energized by a dynamic willingness to fight for their rights and the rights of their students are exercising bold expressions of political power. The power of collective resistance is being mounted in full force against a neoliberal logic that unabashedly insists that the rule of the market is more important than the needs of teachers, students, young people, the poor and those deemed disposable by those with power in our society. Teachers are tired of being relentless victims of a casino capitalism in which they and their students are treated with little respect, dignity and value. They have had enough with corrupt politicians, hedge fund managers and civically illiterate pundits seduced by the power of the corporate and political demagogues who are waging a war on critical teaching, critical pedagogy and the creativity and autonomy of classroom teachers.
Since the 1980s, an extreme form of capitalism — or what in the current moment I want to call neoliberal fascism — has waged a war against public education and all vestiges of the common good and social contract. In addition, this is a war rooted in class and gender discrimination — one that deskills teachers, exploits their labor and bears down particularly hard on women, who make up a dominant segment of the teaching force. In doing so, it not only undermines schooling as a public good, but also weaponizes and weakens the formative cultures, values and social relations that enable schools to create the conditions for students to become critical and engaged citizens.
Schools have been underfunded, increasingly privatized and turned into testing factories that deliver poor students of color to the violence of the school-to-prison pipeline. Moreover, they have also been restructured in order to weaken unions, subject teachers to horrendous working conditions and expose students to overcrowded classrooms. In some cases, the dire working environment and dilapidated conditions of schools and classrooms appear incomprehensible in the richest nation in the world. For instance, as South Carolina teachers go on strike, Hiram Lee reports:
The average salary stands at $10,000 below the national average, while the minimum starting salary is only $30,113 a year…. Working conditions are extremely poor. [In one instance] raw sewage mixed with worms and insects flowed into the hallways of Ridgeland Elementary in Jasper County, where it was tracked into classrooms by students. In other schools, holes in the floors of some classrooms allowed students to see into the classrooms below them. Teachers used old rags and sandbags to prevent a flood of rainwater coming in through cracks in the walls. Libraries were filled with shockingly few books, and those on hand were so outdated that one teacher recalled finding a book that predicted, «One day man will land on the moon.»
What the South Carolina mobilization and the other teacher walkouts across the nation suggest is that these expressions of collective resistance are about both the survival of democracy in Trump’s America and a challenge to the commanding institutions and organizing ideals and principles that make it possible.
The Reclamation of Education as a Public Good
Fortunately, teachers, students, progressive social movements and others are rising up, refusing to be written out of the script of a potentially radical democracy.
Yet, what has often been lost on those who have courageously charted this growing assault on democracy is perhaps its most debilitating legacy: the long-standing and mutually reinforcing attacks on both public education and young people. Such attacks are not new; rather, they have simply intensified under the Trump administration. As a war culture has started organizing all aspects of society, schools have transformed into zones of economic and political abandonment. Increasingly modeled after prisons, schools have become subject to pedagogies of oppression and purged of the experiences, values and creativity necessary for students to expand and deepen their knowledge, values and imagination. Moreover, as state and corporate violence engulfs the entire society, schools have been subject to forms of extreme violence that in the past existed exclusively outside of their doors. Under such circumstances, youth are increasingly viewed as suspects and are targeted both by a gun culture that places profits above student lives and by a neoliberal machinery of cruelty, misery and violence dedicated to widespread educational failure. Instead of imbibing students with a sense of ethical and social responsibility while preparing them for a life of social and economic mobility, public schools have been converted into high-tech security spheres whose defining principles are fear, uncertainty and anxiety. In this view, a corporate vision of the US has reduced the culture of schooling to the culture of business and an armed camp, and in doing so, imposed a real and symbolic threat of violence on schools, teachers and students. As such, thinking has become the enemy of freedom, and profits have become more important than human lives.
Today’s teachers and students are facing not only a crisis of schooling but also a crisis of education.
Public schools are at the center of the manufactured breakdown of the fabric of everyday life. They are under attack not because they are failing, but because they are public — a reminder of the centrality of the role they play in making good on the claim that critically literate citizens are indispensable to a vibrant democracy. Moreover, they symbolize the centrality of education as a right and public good whose mission is to enable young people to exercise those modes of leadership and governance in which «they can become fully free to claim their moral and political agency.»
Rejecting the idea that education is a commodity to be bought and sold, teachers and students across the country are reclaiming education as a public good and a human right, a protective space that should be free of violence, and open to critical teaching and learning. Not only is it a place to think, engage in critical dialogue, encourage human potential and contribute to the vibrancy of a democratic polity, it is also a place in which the social flourishes, in that students and teachers learn to think and act together.
Under the current era of neoliberal fascism, education is especially dangerous when it does the bridging work between schools and the wider society, between the self and others, and allows students to translate private troubles into broader systemic considerations. Schools are dangerous because they exemplify Richard J. Bernstein’s idea in The Abuse of Evil that «democracy is ‘a way of life,’ an ethical ideal that demands active and constant attention. And if we fail to work at creating and re-creating democracy, there is no guarantee that it will survive.»
How the Current Crisis in Education Emerged
Insisting on the right to teach, the right to learn and the right to view schools as a valued public good historically have been radical acts. How did we get to this present moment? Under the regime of neoliberalism, deindustrialization, the tax revolt of the 1970s, and the increasing attack on the social contract and welfare state imposed new burdens on public education at the end of the 20th and the beginning of the 21st centuries.
Schools were increasingly underfunded as inner cities descended into poverty, class sizes increased, poor students dropped out, and schools became more segregated by class and race. Teachers were increasingly deskilled and lost control over the conditions of their labor as lifeless accountability schemes and mind-numbing testing regimes were passed off as reform initiatives under the Bush, Clinton and Obama administrations.
Once the teachers realized that the terrible conditions under which they worked were commonplace they were ready to act regardless of whether they had the support of their unions.
These reforms, while allegedly appealing to educational ideals, especially the assumption that they would help economically underprivileged students, did just the opposite and turned schools largely into imagination-crushing citadels of boredom and conformity. President Bush’s educational policy, the No Child Left Behind Act of 2001, which did a great deal to leave many children behind, was followed by Obama’s policy titled Race to the Top. Unfortunately, Obama simply provided more of the same dead-end approaches to education that had damaged public education for decades.
What is different under the Trump administration is that today’s teachers and students are facing not only a crisis of schooling but also a crisis of education. Trump is upfront in stating without apology that he loves both the uneducated and being uneducated. Not only does he disparage any display of critical intelligence — whether in the critical media, courts or online culture — he has made it clear with his education secretary choice, Betsy DeVos, the billionaire and utterly clueless charter school advocate, that he holds the very notion of public education as a crucial democratic public sphere in low regard.
In a meeting with 2018 teachers of the year, DeVos stuck to her anti-public school, anti-teacher script by stating that she hoped that teachers «would take their disagreements and solve them not at the expense of kids and their opportunity to go to school and learn.» In part, this is code for a broader narrative in which conservatives and liberals for years have been blaming teachers exclusively for students who drop out of school, end up in the criminal legal system, perform poorly academically and distrust authority, among other issues. As if such failures are entirely the fault of teachers, regardless of the defunding of schools, the rise of overcrowded classrooms, the increase in widespread poverty, the starving of the public sector, accelerated attacks on public servants, the transformation of cities into ghost towns, the smashing of teacher unions and the creation of labor conditions for teachers that are nothing short of deplorable. No surprises here. DeVos appears to have a penchant for reaching for the low-hanging rhetorical fruit when it comes to commenting on public schools, teachers and students.
The ideological assault against public schools, teachers and students is now in full force thanks to an alliance among big corporations, billionaires such as the Koch brothers, conservative foundations, business lobbying groups such as the American Legislative Exchange Council (ALEC) and the Trump administration. This alliance seeks to privatize public schools, increase tax breaks for the rich (depriving schools of essential revenue), substitute privately run charter schools for public schools, support voucher programs, cut public services, endorse online instruction and redefine public schools around issues of safety and security, further situating them as armed camps and extensions of the criminal legal system. The question here is why corporations, politicians, hedge fund managers and a horde of billionaires want to destroy public education and inflict irreparable harm on millions of children.
Gordon Lafer, a professor at the University of Oregon, has argued in his book, The One Percent Solution: How Corporations Are Remaking America One State at a Time that the US is a country in decline, characterized by a rise in economic inequality, families unable to support themselves, increased hardships for workers, the decline of social provisions, the evisceration of public goods, restricted voter rights, lowered employment standards, an ongoing attack on social safety nets and a dwindling middle-class. Lafer believes that the war on schools is rooted in a terrifying set of neoliberal policies and that big business is determined to dismantle public education. He argues that
big corporations are … worried … about how to protect themselves from the masses as they engineer rising economic inequality [and] they try to avoid a populist backlash … by lowering everybody’s expectations of what we have a right to demand as citizens…. When you think about what Americans think we have a right to, just by living here, it’s really pretty little. Most people don’t think you have a right to healthcare or a house. You don’t necessarily have a right to food and water. But people think you have a right to have your kids get a decent education.
Teachers Fight Back
Against the current frontal assault on public education and the rights of teachers and students, a new wave of opposition has developed around the nation’s schools that has provoked the public imagination and mobilized mass numbers of students, educators and the public at large. Teachers have been walking out, striking and demonstrating in states across the country. From the initial strike in West Virginia to demonstrations in Colorado, Kentucky, Arizona and North Carolina, and potentially other states including Louisiana, Nevada and South Carolina, teachers are protesting not only low salaries, but also related issues such as, school defunding (prompted by regressive tax measures designed to benefit the rich and corporations), overcrowded classrooms and rising health premiums.
The successful West Virginia strike was especially notable, Kate Aronoff argues, because it was one of the biggest «work actions in recent U.S. history, rebuffing austerity and, at points, even the wishes of their union leaders.» Teachers in West Virginia were under increasing attack by a GOP-controlled legislature and their Republican governor, billionaire coal baron Jim Justice, who colluded to force teachers to pay increasingly higher premiums for their health care, put up with large classes, and endure what Lynn Parramore has described as «increasingly unlivable conditions — including attempts to force them to record private details of their health daily on a wellness app … [while allowing] them no more than an annual 1% raise — effectively a pay cut considering inflation — in a state where teacher salaries ranked 48th lowest out of 50 states.» At the end of a nine-day strike, they negotiated a 5 percent pay increase from the state.
Similar strikes followed in Oklahoma, Kentucky, Arizona and beyond. While all of these strikes addressed issues specific to their states, they shared a number of issues that revealed a broader attempt to undermine public education. In all of these states, teachers made paltry wages «nearly $13,077 below the nationwide average of $58,353 and well below the nationwide high of New York at $79,152.» Many teachers had to work two or three extra jobs simply to be able to survive. In a number of cases, their pension plans were being weakened. Growing pay inequities stretch across two decades for most teachers as they «are contributing more and more toward health care and retirement costs as their pay falls further behind. Teacher pay (accounting for inflation) actually fell by $30 per week from 1996 to 2015, while pay for other college graduates increased by $124.»
There is a direct line between spending cuts for schools and a decrease in taxes for the rich and big corporations. In Oklahoma, taxes had not been raised since 1990, and in 2010 the Republican governor passed «huge breaks for the oil and gas companies» and in 2015 reduced the tax rate to 2 percent with the «cost to the state … estimated at $300 to $400 million per year.» Schools were shockingly underfunded and the consequences for both teachers and students have been devastating. Eric Blanc observes that:
Since 2008, per-pupil instructional funding has been cut by 28 percent — by far the worst reduction in the whole country. As a result, a fifth of Oklahoma’s school districts have been forced to reduce the school week to four days. Textbooks are scarce and scandalously out of date. Innumerable arts, languages, and sports courses or programs have been eliminated. Class sizes are enormous…. Many of Oklahoma’s 695,000 students are obliged to sit on the floor in class.
Meanwhile, Mike Elk reports that the Oklahoma Education Association released a statement saying: «Over a decade of neglect by the legislature has given our students broken chairs in classrooms, outdated textbooks that are duct-taped together, four-day school weeks, classes that have exploded in size and teachers who have been forced to donate plasma, work multiple jobs and go to food pantries to provide for their families.»
All of the states engaged in wildcat strikes, demonstrations and protests have been subject to similar toxic austerity measures that have come to characterize a neoliberal economy. Once the teachers realized that the terrible conditions under which they worked were commonplace in other schools and states and that many other teachers had reached a boiling point, they were ready to act regardless of whether they had the support of their unions. This was another important thread running through demonstrations. The strikes were not initiated by the leadership in the unions, and when they did act, they were too slow to be consequential. As working conditions for teachers deteriorated and the assault on public schools reached fever pitch, teachers bypassed their unions while using social media to speak to other teachers, communicate across national boundaries and educate a wider public.
The striking teachers hopefully will make clear that there is no contradiction between the struggle for quality public schools and fighting other injustices.
In spite of a number of attacks by conservative politicians such as Kentucky Gov. Matt Bevin, who stated that teachers were displaying «a thug mentality,» the striking teachers gained broad popular support. It is hard to miss the irony here of the neoliberal apostles of austerity labeling teachers as losers, given that many teachers have extra jobs to support themselves and use their own money to provide books, basic resources and in some cases, even toilet paper for their students. Recent findings by the National Center of Educational Statistics show that 94 percent of teachers pay out of their own pockets for school supplies — such as notebooks, pens and paper — which amounts on average to $480 annually. The real losers are the politicians who defund public schools, deskill teachers, force students to put up with repressive test-taking pedagogies «while whittling away at [teacher] salaries, supplies, tenure arrangements, and other union protections … lengthening teaching hours, [and] reducing vital prep periods.» This is a neoliberal script for the social abandonment of public goods, the termination of the democratic ethos and the precondition for the rise of an American version of fascism. What is particularly promising about these widespread protest movements is that they have the potential to move public consciousness toward a wide-ranging recognition in which the assaults on public schooling will be understood as part of a larger war on schools, on youth, and on the very possibility of teaching and learning, and that these struggles cannot be separated.
The use of the social media by the teachers was particularly effective in getting their message out. Individual teachers talked publicly about having to donate blood, visit food pantries and teach with textbooks that were 10 years old. Images of broken chairs and desks, along with rodents infesting classrooms, and students complaining about books that were held together with tape offered a compelling visual archive of not only dilapidated schools, impoverished classrooms and overburdened students, but also a political system in which Republican governors and legislators were willing to implement economic policies that slashed the taxes of the rich and big corporations at the expense of public schools, teachers and students.
Arizona is another case in point: Not only does it have abysmal teacher pay, it is also a state that lacks collective bargaining rights. Debbie Weingarten offers a succinct summary of the effects of budget cuts on Arizona schools, teachers and students:
During the Recession, the Arizona state legislature cut $1.5 million from public schools, more than any other state, leaving Arizona schools more than $1 billion short of 2008 funding…. Arizona currently ranks 49th in the country for high school teacher pay and 50th for elementary school teacher pay. When adjusted for inflation, teacher wages have declined more than 10 percent since 2001. Per-student spending in Arizona amounts to $7,205, compared with the national average of $11,392. There are currently 3,400 classrooms in Arizona without trained or certified teachers, and the state has over 2,000 teacher vacancies.
Arizona teachers ended their strike after a six-day walkout, and while they did not get everything they demanded, the state gave them a «20 percent raise by 2020 and investing an additional $138 million in schools.» Most importantly, the Arizona teacher strike — along with other strikes and teacher walkouts — proved not only the power of organized labor prompted by the radical initiatives of teachers willing to fight for their rights even if the unions do not support them, but also the growing support of a public unwilling to allow neoliberal fascism destroy all vestiges of the public good, especially schools. As Jane McAlevey observes:
Remarkably, these strikes have garnered overwhelming support from the public, despite years of well-funded attacks on teachers’ unions. In a recent NPR/Ipsos poll, just one in four respondents said they think teachers are paid enough, and three-quarters said teachers have the right to strike. Remarkably, this support cut across party lines. «Two thirds of Republicans, three-quarters of independents and nearly 9 in 10 Democrats» support the teachers’ right to strike, the poll showed.
Protests against the gutting of teacher salaries, pensions and health care benefits are not simply about school budgets. They are also about a larger politics in which big corporations and the financial elite have waged a war on democracy and instituted polices that produce a massive redistribution of wealth upward into the hands of the ruling elite. Energized young people and teachers are creating a new optics for both change and the future.
A Mass Movement to Resist Neoliberalism
The teacher strikes and walkouts point to a grassroots movement that will no longer allow the apostles of neoliberalism, the Republican and Democratic parties, and the financial elite to ruthlessly take apart public education. Implicit in the current walkouts and strikes is the necessity of such groups to learn from each other, share power and work to create a mass-based social movement. This type of social formation is all the more crucial given that no one movement or group organized around singular issues can defeat the prevailing concentrated economic and political forces of casino capitalism. Given the public support the striking teachers have received, it is crucial that such a struggle connect the struggle over schools to a broader struggle that appeals to parents who still view public schooling as one of the few avenues their children have for economic and social mobility. At the same time, it is crucial for the striking teachers to make the case to a larger public that without a quality and accessible public education system, the protective and crucial public spaces provided by a real democracy are endangered and could be lost.
Teachers, young people and others are creating both a new and potentially radical language for politics and educational reform. Given the authoritarian times in which we live, this language is desperately needed by a society facing an impending crisis of memory, agency and democracy. If American society is to offset the deeply anti-democratic populist revolt that has put a fascist government in power in the United States, progressives and others need a new language that connects the crisis of schooling to the crisis of democracy while at the same time rejecting the equation of capitalism and democracy. The attack on public schooling is symptomatic of a more profound crisis that involves the extension of market principles to every facet of power, culture and everyday life. Public schooling is under siege along with the values and social relations that give viable meaning to the common good, economic justice and democracy itself.
Striking teachers have recognized that any radical call for educational reform demands more than a call for salary increases, adequate pensions and school resources. Demands for radical educational reforms also necessitate what Martin Luther King Jr. once called a «revolution of values.»
This would suggest a radical reworking of the language of freedom, autonomy, equality and justice that refused to be articulated with the neoliberal spheres of privatization, consumer culture, deregulation, and a politics of terminal exclusion, disposability and the acceleration of the unwanted. Schools can no longer be viewed as zones of political, economic and social abandonment. The striking teachers across the nation are making clear that everyone has the right to live in both an educated society and a democracy, and that you cannot have one without the other. Hopefully, they can learn from past historical battles while leading the struggle to merge a number of different movements for a radical democracy. One option in doing so is to build support for what Michael Lerner has called developing a global Marshall Plan in order to redistribute wealth, build infrastructures, expand public goods, create the conditions for environmental responsibility, and eliminate the capitalist structural and economic conditions that prevent such movements, policies and investments from taking place.
The striking teachers hopefully will turn a moment into a movement, and in doing so, make clear that there is no contradiction between the struggle for quality public schools and fighting other injustices such as poverty, mass incarceration, unchecked inequality, massive student debt, systemic violence, escalating militarization of society and the war on the planet. Across the nation, teachers, students and other educators have demonstrated that democratic ideals, even under conditions of neoliberal tyranny and a dystopian mode of education, can be recognized, embraced and struggled over. Education is a symptom of a deeper, dangerous and more fundamental crisis that demands analyses and actions aimed at root causes. The brutal neoliberal fascism of the moment can only be defeated if teachers, young people and grassroots activists develop alliances and develop new topographies for addressing the root causes of the current brutal despotism and loss of faith in democratic institutions — that means a strong anti-capitalist movement.
The struggle over public education has ignited new modes of criticism that contain the potential to build a mass movement from the bottom up and translate single-issue demands into wider expectations for social change and alternative visions for a democratically socialist United States. Hopefully, this movement will continue to be guided by the kind of energy and insight that Ursula K. Le Guin once articulated: «We will not know our own injustice if we cannot imagine justice. We will not be free if we do not imagine freedom. We cannot demand that anyone try to attain justice and freedom who has not had a chance to imagine them as attainable.»
Source:
http://www.truth-out.org/news/item/44564-striking-teachers-beat-back-neoliberalism-s-war-on-public-schools

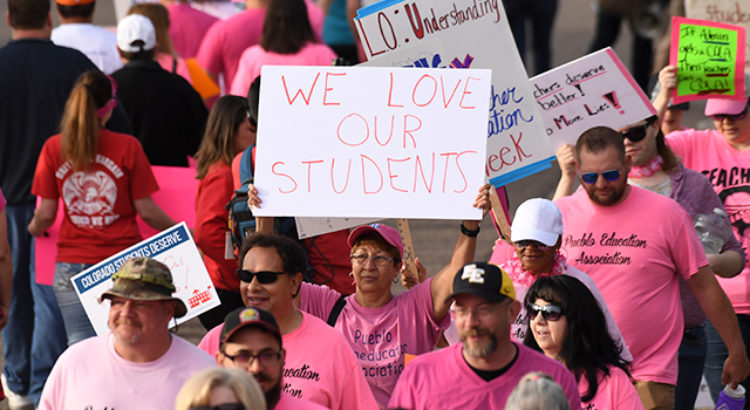











 Users Today : 8
Users Today : 8 Total Users : 35460977
Total Users : 35460977 Views Today : 9
Views Today : 9 Total views : 3420445
Total views : 3420445