By Kyle Spencer
Fraternity members at Louisiana State University adhere to age-old rituals, shrouded in secrecy, that dictate how they gather, greet each other and initiate their young pledges.
But when they return to campus in the fall, one ritual will be drastically different: They will face much more severe consequences for dangerous hazing incidents.
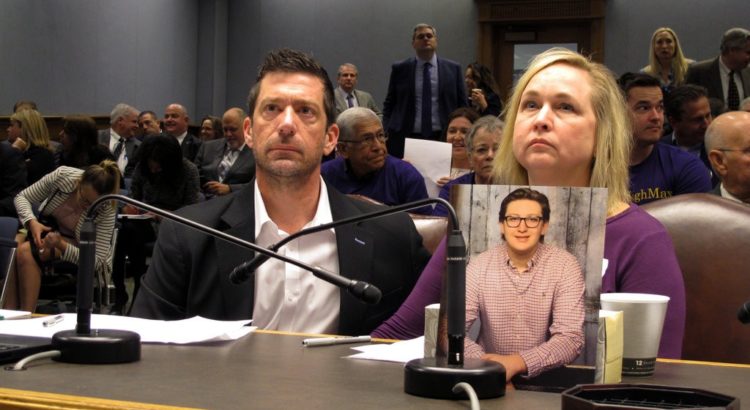
In May, eight months after the death of Maxwell Gruver, a freshman pledge at the university’s now banished Phi Delta Theta fraternity chapter, Gov. John Bel Edwards of Louisiana signed into law an anti-hazing bill that would make it a felony for those involved in hazing that resulted in death, serious bodily harm, or life-threatening levels of alcohol. And students found guilty could land in a Louisiana jail for up to five years.
The new law represents an important departure for Louisiana, which once had some of the most lenient anti-hazing laws in the nation. But it also reflects renewed efforts around the country — in state legislatures, inside courthouses and on campuses — to prevent the hazing injuries and deaths that have plagued college campuses for decades.
“Realistically, the answer is regulation and reform,” John Hechinger, the author of “True Gentlemen: The Broken Pledge of America’s Fraternities,” said during a panel on Greek life last week at The New York Times Higher Ed Leaders Forum. “That is really the only possibility.”
There has been at least one school-related hazing death each year in the United States since 1961, according to Hank Nuwer, a Franklin College journalism professor and the author of multiple books on hazing. Most, but not all, have occurred during fraternity initiation events.
But in 2017, four students, including Mr. Gruver at L.S.U., Tim Piazza, a 19-year-old at Pennsylvania State University and Andrew Coffey, a 20-year-old at Florida State University, lost their lives in hazing-relating incidents. Mr. Coffey died on a fraternity house couch after drinking an entire bottle of bourbon during Big Brother Night. In each case, multiple students were charged.
This fall, Penn State President Eric J. Barron, who appeared on the panel with Mr. Hechinger, said that the incident on his campus had been a “horrible tragedy,” but one that had spurred new interest in reform.
This past year, Dr. Barron banned 13 organizations from his campus and instituted 15 reforms, including switching disciplinary oversight of the institutions from a Greek governing council to university administrators, requiring newcomers to take a pledge about their actions inside their organizations and deferring the initiation process for freshmen until later on in the school year, so they can develop new friends and interests before being faced with hazing.
This winter, officials at Florida State University started a hazing education initiative and increased staff members charged with monitoring Greek life. And at Louisiana State, President F. King Alexander proposed 28 reforms, including a requirement that chapters hire house managers.
College administrators are also beginning to look at the problem collectively. At a meeting in Chicago this spring, representatives from 31 colleges and universities explored ways to garner more cooperation from national Greek organizations, which can resist university oversight.
Dr. Barron is pushing an online safety database that will record incidents at chapters around the country, indicate which institutions are doing exemplary work in their communities and which are experiencing alarming trends.
Penn State and many other universities already have, or are instituting, their own report cards.
The high profile nature of the cases is also impacting state capitals. Pennsylvania, like Louisiana, is expected to soon pass an anti-hazing law that would make death by hazing a felony.
New Mexico has also been exploring the idea.
In Tennessee, state representative John DeBerry Jr. floated a bill that would ban fraternities altogether in the state.
Mr. Hechinger says fighting to make fraternities safer is probably a better use of critics’ energy, as it is unlikely that fraternities will be banned on public campuses where they are powerful.
“If we were going to create a higher education system from scratch, would we have organizations that year after year kill a student? Probably not,” he said at the conference. “But they are very ensconced in higher education, and if you try to do some kind of ban, which is often what people are asking, you run the risk of underground behavior.”
Source of the article: https://www.nytimes.com/2018/06/05/education/learning/colleges-fraternities-laws.html





 Users Today : 194
Users Today : 194 Total Users : 35459789
Total Users : 35459789 Views Today : 354
Views Today : 354 Total views : 3418326
Total views : 3418326