By Peter Anti Partey (IFEST – Ghana)
Education is a merit good. Countries spend huge sums of their revenue on education. Research abound on the impact of education in relation to poverty alleviation. Empirically, education is the mechanism that is used to transform economies. It is therefore not surprising that most countries in the developing world are seriously pursuing the knowledge economy agenda. This scientifically explains the numerous interventions that governments over the years have made in the Ghanaian education sector. Paramount among them is the introduction of the Free Senior High School policy which sought to open access to thousands of students who would genuinely not have had access to secondary education due to financial constraints.
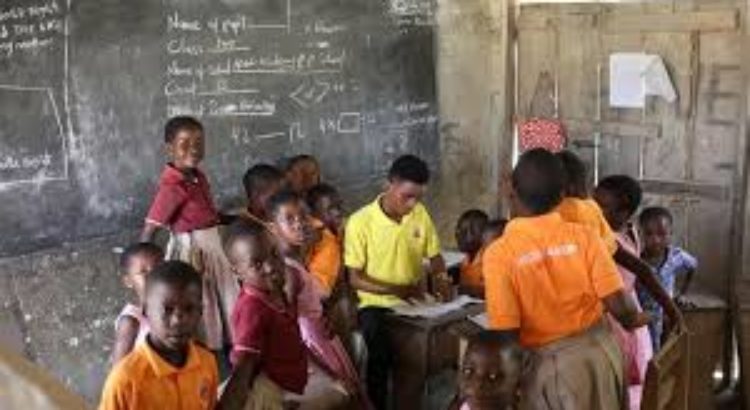
Though lots seem to have been carried out in the education sector, the advent of COVID-19 seems to have revealed some endemic problems in our educational system. The closure of schools in the country has affected close to 10 million students at all levels of the education ladder. To mitigate the impact of the closure of schools and ensure continuity in learning coupled with prior experience from previous pandemics in other countries, government through the Ministry of Education rolled out different forms of interventions. These include providing free online library services, online learning platform (icampusgh.com) and virtual learning being aired on various television and radio station in the country. Again, the Ministry has facilitated the zero-rating of most educational platforms for most of the tertiary institutions in the country. This intervention is meant to ensure that the cost of data does not serve as a hindrance to any student who would want to access online education in Ghana. These interventions are all geared towards the objective of ensure that, academic work is carried out during the period of the pandemic.
Despite these efforts by the Ministry, our development trajectory has made it practically impossible for all students to benefit fully from these interventions. This is because, the extent of digital divide in the country is so huge that, even the provision of zero-rated online educational platforms will mean nothing to majority of students who do not have access to any electronic device to benefit fully from this intervention. Also, most students and teachers are not technologically savvy to be able to utilize these platforms fully. This brings to the fore the concern that, as a people we have a penchant for policy sloganeering instead of policy robustness. A country with an ICT policy in education which also rolled out a policy of “one laptop per child” between 2009 and 2012 should not be struggling to reach the masses of students when it matters most. But characteristically of us, we politicized the distribution of the laptops and did not pursue the policy after some time. Consequently, in 2020, most of our students in sub-urban and rural Ghana are finding it difficult to join their colleagues to access various e-learning platforms.
Again, until recent developments, our educational system had been built solely on examinations. The 9 or 12 years of education of the child meant nothing if he/she fails the Basic Education Certificate Examination or the West African Senior School Certificate Examination (WASSCE) respectively. This mode of assessment has created a dilemma, I dare say, in the minds of all relevant stakeholders as to the way forward for our students since we are at the end of the academic year and students would still have to progress to the next level of their educational journey. Globally, three models have been adopted by various countries depending on their unique circumstances to circumvent the issue of school examination and progression during this period. These models are: Cancellation of examinations, Postponement of examinations and Reviewing of the examination format. Countries that philosophically place much emphasis on the total educational journey of the student have resorted mostly to Models 1 and 3 (Cancellation of examination and Reviewing of examination format). For instance, in Norway, examinations have been cancelled for students in both junior high and high school. This was made possible since written exams forms only 20% of the final grading of the student. In Northern India, students from grades 1 – 8 will be progress to the next level without any examination. In the USA, SAT has been cancelled leading to the review of the admission criteria for entering the universities whereas emphasis has been placed on the students’ course work and other relevant modalities.
In Ghana however, there is still uncertainty as to the way forward since we have adopted model 2. The question is; “for how long would these examinations be postponed?” It is true that, WASSCE is a sub-regional examination and hence a determination would have to be made by the examination body, however, one would want to ask, what proposals have the government and the Ministry in charge of education made to the relevant authorities as to the unique way we would want to handle this in our education sector. Clarity and a clear cut roadmap with feasible timelines would help students, parents and all relevant stakeholders plan accordingly (this should be carried out bearing in mind the challenges of the school placement process and various timelines in our educational system). There have been proposals to aggregate the 30% school-based assessment used by WAEC for grading students. I must say that, this proposal by all standards, violate the principles of assessment as espoused by experts because of issues of standardization, reliability, validity, clarity, significance etc. which mostly might lead to under-prediction of grades especially for students of disadvantaged backgrounds.
The proposal would therefore be to adopt Model 3 and review the examination format for BECE candidates focusing on the core subjects and resorting to an online examination well-structured to meet the needs of all candidates. Their scores coupled with the assessment from their schools can be used to place them for their secondary education. This can easily be done since the principal focus of that examination is for placement. For those writing WASSCE, the principal objective of that certificate is continuation to tertiary institutions. It will therefore be prudent for the universities to review their admission process and introduce an entrance examination for those who would want to continue their education. The certificate can be awarded when issues normalize for all students after they have sat for that comprehensive examination. The advantage will be that, students will be ready for the next level of their education and would not have to wait for their certificates. These are proposed to ensure that, the already distorted academic calendar does not exacerbate.
For tertiary education, the surest way is for the various tertiary institutions to revamp their online education platforms and reach their students who are residential and non-residential. The Ed-tech take off propelled by COVID-19 should be embraced by our institutions of higher learning. The Student Loan Trust Fund (SLTF) should be thinking of providing additional support to students to enable them own the digital devices needed for their learning. The proposal is to open up a request form for students who would need such digital devices (android phones, laptop, etc.) to apply for and be supplied with, as part of their student loan.
The educational sector is hit also from the front of the private schools’ setup. Most private schools have not been able to pay their staff and some have even resort to downsizing and termination of appointment of teachers. Recently, the private schools professional body appealed to government to assist them with a stimulus package to enable them meet their recurrent expenditure. Though this is a call in good faith, adherence to it is likely to open the flood gate for all others in the private sector to also seek for support from the already tight government revenue. It is therefore advocated that, government should facilitate so that these private schools can access financial support from both local and international institutions on the basis of their ability to repay within a reasonable timeframe. I would also appeal to parents who still owe fees to redeem themselves. One way that these private schools can continue to ask for an agreed school fees from parents would be to find ways of engaging the students online. This even though not novel, would help them come to some agreement for an amount to be paid for such services rendered.
Change is difficult. However, when the opportunity presents itself, authorities should gladly take advantage of the circumstances and effect the needed change. This is the time to redefine education in Ghana. We have lagged in our quest to use technology in our educational system. While most educational institutions globally were quickly switching to their various online platforms to enable them continue to deliver education to their students, we are yet to fully achieve same. A call to our policy makers to be guided by the principles of equity and fairness in rolling out policies bearing in mind the level of disparities in our society should never be in vain after life return to normalcy. Our social support systems are weak and that is what might lead to our total destruction and not a pandemic.
Source of the article: Equipo de Ove





 Users Today : 163
Users Today : 163 Total Users : 35459758
Total Users : 35459758 Views Today : 310
Views Today : 310 Total views : 3418282
Total views : 3418282