El título de la saga animada autóctona más divertida e iconoclasta de las que en Cuba circulan de manera alternativa hace algunos años, deja aparentemente claro de qué va todo. En Danny y el club de los berracos, el protagonista y su círculo íntimo de amigos adolescentes, son seres (como el macho del cerdo) sexualmente activos, efervescentes, incendiarios, obcecados por el tema erótico y la sexualidad turgente que apenas reprimen.
Pero no es el sexo el tema de esta serie. A la altura de su quinto capítulo, ya disponible en el Paquete Semanal (ni pensar que transmitido en la televisión estatal, demasiado pacata para tanto atrevimiento) la obra de Víctor Alfonso Cedeño, Vito, toma altura y comienza a navegar en las movidas aguas de la valoración social.
Si no ha visto el capítulo aún (no se moleste en buscarlo, está al final de esta entrada) esta es una Spoiler Alert: aquí se lo contaré casi todo. Si ya lo vio, comparta conmigo sus propias claves e interpretaciones.
Una escuela de adolescentes en plena pubertad es el escenario de la trama, y una conversación en los baños lo desencadena todo.
El perfil carismático por excelencia es Calixto, el más listo de todos, incrédulo y emprendedor, con mucho talento para todo lo que implique ir contra la corriente, quien esta vez se postula para presidente de la federación de estudiantes.
El Chino, por su parte, representa a un mulato libidinoso y metrosexual, que se afeita las axilas. Mauricio, en cambio, es la representación animada de la militancia política, la puesta en escena de agendas, bolígrafos y órdenes del día, movilizado por el espíritu revolucionario del cambio desde el respeto absoluto a una ética e ideología incompatibles con la corrupción pero colindantes con la demagogia. Y por supuesto, Danny, el personaje contemplativo, dubitante, es quien sirve de amalgama existencial y balance a su grupo de amigos endocrinos.
Hay un realismo casi naturalista en los detalles de esta producción sin vocación pedagógica: ahí está la posición escatológica pero precavida de agacharse al momento de defecar en un sanitario inmundo, la dependencia incipiente hacia el móvil y los videojuegos, la prédica gastada de los cuadros de las organizaciones políticas y estudiantiles, los cables pelados que sirven de interruptores eléctricos improvisados.
Como toda obra dramática aparecen también personajes antagónicos, acaso negativos. Cumplen la función de entorpecer el transcurrir de las peripecias de la obra, rocambolesca, pero no por ello son inverosímiles.
Silvio y Mirelis, los dirigentes estudiantiles, militantes ortodoxos y oportunistas, esperan su momento para dar el zarpazo y desplazar a Mauricio de la presidencia de la organización. Se resisten taimados al cambio de estructuras, funcionamiento y mentalidades. Intentan preservar intactos determinados modos de hacer política, porque les conviene defender el statu quo sin objeciones ni iniciativas propias. Los dos desplazados por la iniciativa de Calixto llegan a practicar el colaboracionismo y la delación ante las autoridades policiales, a cambio de poder dar curso a la revancha. Toda una alegoría.
Pero más importante que los personajes son los cuestionamientos de este cortometraje que enjuicia no tanto al sistema educativo, sino a la sociedad cubana actual en su conjunto.
La crítica a muchos problemas y situaciones reales subyacen bajo el entramado argumental de una historia simpática, que no se arruga y cuida el ritmo narrativo. El corto habla sobre todo de la necesidad de un liderazgo de nuevo pulso, a todos los niveles, donde la capacidad de reacción, el pragmatismo económico, la conciliación, el diálogo real, la convivencia armoniosa y el respeto a la diversidad, le corten el paso al inmovilismo ideológico y político, del signo que sea.
En las ideas de Calixto hay una necesidad de apelar en la estimulación a recompensas materiales, palpables, para que sirvan de incentivo a los individuos, más allá de la tradicional “emulación socialista”, que prioriza los homenajes y reconocimientos simbólicos pero que descuida cubrir las ambiciones, expectativas, intereses, objetivos y urgencias del día a día.
Por eso se puede tornar polémico para algunos este capítulo: en la ficción de Vito se juega con nuevo modelos y modos de gestión económica privada, llevadas al ámbito de las políticas públicas, quizás uno de los cuestionamientos que usarán en su contra los detractores de la serie.
Más “competitivas”, las alternativas que propone implementar el personaje de Calixto para tener lista la escuela ante la inspección de la ministra pasan por hacer partícipes del proceso de cambio a los agentes sociales más activos: los emprendedores, un planteamiento herético que expone las dudas y resquemores sistémicos ante su emergencia e impacto económico, a corto y mediano plazo.
Pero no es una loa al individualismo el capítulo. Solo con la acción del colectivo se podrán asfaltar las cubiertas, higienizar las áreas verdes, limpiar el piso, desempolvar la iconografía revolucionaria que aparece adosada a la pared. También se precisa un cambio de perspectivas, para que el proceso inversionista contemple la posibilidad de pintar murales concebidos en una estética atractiva, urbana, que no recicle esperpentos épicos mal representados.
Luego de seguir las peripecias de la trama, me quedo con la impresión de que Vito ha recompuesto a discreción el mito del hombre nuevo, uno sin aires de superioridad ni trascendencia monolítica, menos almidonado ahora, más astuto, asertivo, eficaz, inteligente, práctico, respetuoso, tolerante. Humano.
Para el autor, joven multipremiado y animador por su cuenta, el desafío consistirá en continuar la serie de una manera alternativa, autónoma en lo económico, independiente desde una posición ética e ideológica, sin concesiones a ningún productor institucional que quiera diluir el carácter crítico de una saga que precisa, cuando menos, algo de financiamiento, dinero, aunque sea para pagarles a los amigos que pusieron las voces a los personajes y arriesgaron el cuello bajo el cuchillo del porquerizo primerizo.
Por lo pronto, el Dany 5 recibió en la 15 Muestra Joven ICAIC un premio colateral de la Fundación Ludwig: una Beca de Creación a favor de La Casita del Lobo, la productora que él ha lanzado. Quizás ayude al parto de un Dany 6.
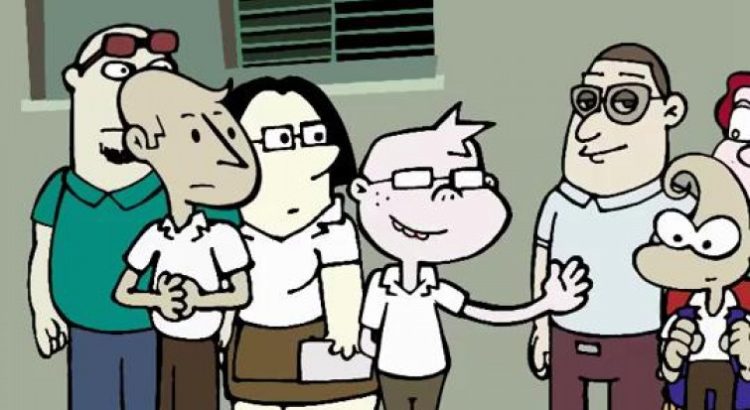

![Dany 5. Calixto presidente[18-21-39]](http://oncubamagazine.com/wmag/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/Dany-5.-Calixto-presidente18-21-39.jpg)






















 Users Today : 40
Users Today : 40 Total Users : 35459946
Total Users : 35459946 Views Today : 46
Views Today : 46 Total views : 3418511
Total views : 3418511