Americans live in a historical moment that annihilates thought. Ignorance now provides a sense of community; the brain has migrated to the dark pit of the spectacle; the only discourse that matters is about business; poverty is now viewed as a technical problem; thought chases after an emotion that can obliterate it. The presumptive Republican Party presidential nominee, Donald Trump, declares he likes «the uneducated» — implying that it is better that they stay ignorant than be critically engaged agents — and boasts that he doesn’t read books. Fox News offers no apologies for suggesting that thinking is an act of stupidity.
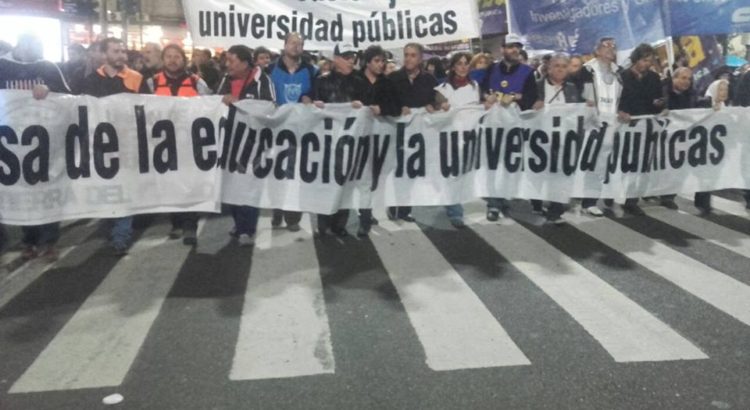
A culture of cruelty and a survival-of-the-fittest ethos in the United States is the new norm and one consequence is that democracy in the United States is on the verge of disappearing or has already disappeared! Where are the agents of democracy and the public spaces that offer hope in such dark times? Many are in public schools — all the more reason to praise public school teachers and to defend public and higher education as a public good.
Public schools and higher education are «dangerous» because they hold the potential to serve as laboratories for democracy.
For the most part, public school teachers and higher education faculty are a national treasure and may be one of the last defenses available to undermine a growing authoritarianism, pervasive racism, permanent war culture, widening inequality and debased notion of citizenship in US society. They can’t solve these problems but they can educate a generation of students to address them. Yet, public school teachers, in particular, are underpaid and overworked, and lack adequate resources. In the end, they are unjustly blamed by right-wing billionaires and politicians for the plight of public schools. In order to ensure their failure, schools in many cities, such as Detroit and Philadelphia, have been defunded by right-wing legislators. These schools are dilapidated — filled with vermin and broken floors — and they often lack heat and the most basic resources. They represent the mirror image of the culture of cruelty and dispossession produced by the violence of neoliberalism.
Under the counterfeit appeal to reform, national legislation imposes drill-and-test modes of pedagogy on teachers that kill the imagination of students. Young people suffer under the tyranny of methods that are forms of disciplinary repression. Teachers remain powerless as administrators model their schools after prisons and turn students over to the police. And in the midst of such egregious assaults, teachers are disparaged as public servants.
To read more articles by Henry A. Giroux and other authors in the Public Intellectual Project, click here.
The insecure, overworked adjunct lecturers employed en masse at most institutions of higher education fare no better. They have been reduced to an army of indentured wage slaves, with little or no power, benefits or time to do their research. Some states, such as Texas, appear to regard higher education as a potential war zone and have passed legislation allowing students to carry concealed weapons on campus. That is certainly one way to convince faculty not to engage in controversial subjects with their students. With the exception of the elite schools, which have their own criminogenic environments to deal with, higher education is in free fall, undermined as a democratic public sphere and increasingly modeled after corporations and run by armies of administrators who long to be called CEOs.
All the while the federal government uses billions of dollars to fuel one of the largest defense and intelligence budgets in the world. The death machine is overflowing with money while the public sector, social provisions and public goods are disappearing. At the same time, many states allocate more funds for prisons than for higher education. Young children all over the country are drinking water poisoned with lead, while corporations rake in huge profits, receive huge tax benefits, buy off politicians and utterly corrupt the political system. Trust and compassion are considered a weakness if not a liability in an age of massive inequities in wealth and power.
In the midst of what can only be viewed as a blow against democracy, right-wing Republicans produce slash-and-burn policies that translate into poisonous austerity measures for public schools and higher education. As Jane Mayer points out in Dark Money, the Koch brothers and their billionaire allies want to abolish the minimum wage, privatize schools, eliminate the welfare state, pollute the planet at will, break unions and promote policies that result in the needless deaths of millions who lack adequate health care, jobs and other essentials. Public goods such as schools, according to these politicians and corporate lobbyists, are financial investments, viewed as business opportunities. For the billionaires who are the anti-reformers, teachers, students and unions simply get in the way and must be disciplined.
We need to invest as much, if not more, in education as we do in the military-industrial complex.
Public schools and higher education are «dangerous» because they hold the potential to serve as laboratories for democracy where students learn to think critically. Teachers are threatening because they refuse to conflate education with training or treat schools as if they were car dealerships. Many educators have made it clear that they regard teaching for the test and defining accountability only in numerical terms as acts that dull the mind and kill the spirit of students. Such repressive requirements undermine the ability of teachers to be creative, engage with the communities in which they work and teach in order to make knowledge critical and transformative. The claim that we have too many bad teachers is too often a ruse to hide bad policies and to unleash assaults on public schools by corporate-driven ideologues and hedge fund managers who view schools strictly as investment opportunities for big profits.
We need to praise teachers, hold them to high standards, pay them the salaries they deserve, give them control over their classrooms, reduce class sizes and invest as much, if not more, in education as we do in the military-industrial complex. This is all the more reason to celebrate and call attention to those teachers in Chicago, Detroit and Seattle who are collectively fighting against such attacks on public schools. We need to praise them, learn from them and organize with them because they refuse to treat education as a commodity and they recognize that the crisis of schooling is about the crises of democracy, economic equality and justice. This is not a minor struggle because no democracy can survive without informed citizens.
Neoliberal education is increasingly expressed in terms of austerity measures and market-driven ideologies that undermine any notion of the imagination, reduce faculty to an army of indentured labor and burden students with either a mind-numbing education or enormous crippling debt or both. If faculty and students do not resist this assault, they will no longer have any control over the conditions of their labor, and the institutions of public and higher education will further degenerate into a crude adjunct of the corporation and financial elite.
Clearly, it is time to revisit Mario Savio’s famous speech at Berkeley in 1964 when he called for shutting down an educational system that had become odious. In his own words:
There comes a time when the operation of the machine becomes so odious, makes you so sick at heart, that you can’t take part, you can’t even passively take part; and you’ve got to put your bodies upon the gears and upon the wheels, upon the levers, upon all the apparatus, and you’ve got to make it stop. And you’ve got to indicate to the people who run it, the people who own it, that unless you’re free the machine will be prevented from working at all.
Savio’s call to resistance is more relevant today than it was then. Public schools not only mimic the injustices of an oppressive economic system, but also funnel poor youth of color into the criminal legal system. The good news is that there is an echo of outrage and resistance now emerging in the United States, especially among young people such as those in the Black Lives Matter movement.
If the major index of any democracy is measured by how a society treats its children, the United States is failing. Fortunately, more and more people are waking up and realizing that the fight for public schooling is not just about higher salaries for teachers; it is about investing in our children and in democracy itself. At the same time, we live in what author Carl Boggs and others have called a permanent warfare state, one in which every space appears to be a battlefield, and the most vulnerable are viewed not only as an imminent threat, but also as the object of potential violence. This suggests that the battle of education must become part of a wider political struggle. This is a struggle that connects assaults on education with the broader war on youth, police violence with the militarization of society and specific instances of racist brutality with the unchecked exercise of the systemic power of finance capital. But the struggle will not be easy.
If the major index of any democracy is measured by how a society treats its children, the United States is failing.
Beneath all of the current brutality, racism and economic predation, there is some hope inspired by the generation of young people who are protesting police violence and the attack on public and higher education and working hard to invent a politics that gets to the root of issues. There is also a glimmer of possibility in those youth who have supported Bernie Sanders but are really demanding a new and more radical definition of politics: Their vision far surpasses that of the left-centrists and liberals of the Democratic Party.
Elections are the ruse of capitalism, and that has never been more clear than at the present moment. On the one side we have Hillary Clinton, a warmonger, a strong supporter of the financial elite and a representative of a neoliberalism that is as brutal as it is cruel. On the other side we have Donald Trump, a circus barker inviting Americans into a den of horrors. And these are the choices that constitute democracy? I don’t think so.
Collective self-delusion will only go so far in the absence of an education system that offers a space for critical learning and dissent, and functions as a laboratory for democracy. There is a tendency to forget in an age dominated by the neoliberal celebration of self-interest and unchecked individualism that public goods matter, that critical thinking is essential to an informed public and that education at the very least should provide students with unsettling ruptures that display the fierce energy of outrage and the hope for a better world.
But a critical education has the capacity to do more. It also has the power not only to prevent justice from going dead in ourselves and the larger society, but also, in George Yancy’s poetic terms, to teach us how to «love with courage.» Hopefully, while education cannot solve such problems, it can produce the formative cultures necessary to enable a generation of young people to create a robust third party — a party fueled by social movements demanding the economic and political justice that could allow a radical democracy to come to life.













 Users Today : 5
Users Today : 5 Total Users : 35460497
Total Users : 35460497 Views Today : 15
Views Today : 15 Total views : 3419373
Total views : 3419373