Japan/April 03, 2018/By: MICHAEL HOFFMAN*/Source: https://www.japantimes.co.jp
Poverty comes in many forms but one color: gray.
There is the poverty of the poor, the poverty of the rich, the poverty of the academically under-qualified, the poverty of the academically over-qualified. The poverty of the poor pretty much speaks for itself. The riches of the rich may be deceptive.
The biggest drain on them is education for the kids. Luxuries and pleasures can be sacrificed, but to compromise where the children are concerned is (or is seen to be) to deprive them of the leg-up they need (or are seen to need) to gain a foothold in life.
What high schools are open to graduates of inferior elementary schools? Inferior ones. What universities are open to graduates of second-rate high schools? Second-rate ones. What kind of career is open to graduates of merely ordinary universities? A merely ordinary one. The consequent financial strain can be felt as a kind of poverty.
If it’s true of the rich, how much more so of the poor. The high cost of education is considered a main cause of the sunken birth rate. If educating your children as the economy demands its top tier be educated requires means beyond the average, means beyond you, childlessness might well seem the more responsible option.
There’s education and education. Motives for acquiring it vary. It can be a quest for knowledge or a quest for credentials. The former is problematic. Shukan Gendai magazine tells some cautionary tales.
“Kyoko-san,” 27, studied fine arts. It was her passion. She’d learn the subject, then teach it. Undergraduate school, graduate school, post-grad school. Hard at work on her Ph.D. thesis, she suddenly noticed something: Students graduating ahead of her weren’t getting jobs.
Stupid of her not to notice before! Absorption in your studies can blind you to earthier realities. Panicking, she put aside her thesis and threw herself into job-hunting. Nothing. Universities were over-staffed, the private sector had no room for her. She eventually landed a job at a small small-town rural arts museum. The work is routine and she feels her expert knowledge rotting within her, but at least she can feed herself.
Not every one is so lucky. “Nakamura-san,” 29, is a Ph.D. scientist struggling to repay a ¥6 million student loan on a ¥2 million-a-year salary. The good news is that his employer is a university and his job description includes the word “research” — followed, unfortunately, by the word “assistant,” which translates into part-time status and lab chores far from the cutting edge.
Maybe in 10 years he’ll get an assistant professorship. Or maybe not — in which case he’ll be 40 years old and nowhere. In the meantime, he lives in a ratty ¥40,000-a-month apartment, eats at the university cafeteria and wonders, “How long can I take this?” It’s enough to make the private sector look attractive — but an exploratory foray into it showed that the private sector did not return the compliment. Knowledge beyond a certain range of commercial exploitability, comments Shukan Gendai, is to the private sector the rough equivalent of otaku-hood.
“Takada-san,” 26, is pursuing a doctorate in literature at the University of Tokyo. He’s learning something the great books don’t teach — to wit: “To get anywhere in research you need connections. I didn’t know that when I started. You need to develop relationships with influential professors who can boost your career.
“So, I get involved in academic meetings, I help out at the reception desk, I coach visiting overseas students. … In short, I’m so busy maneuvering behind the scenes that I have no time to study.”
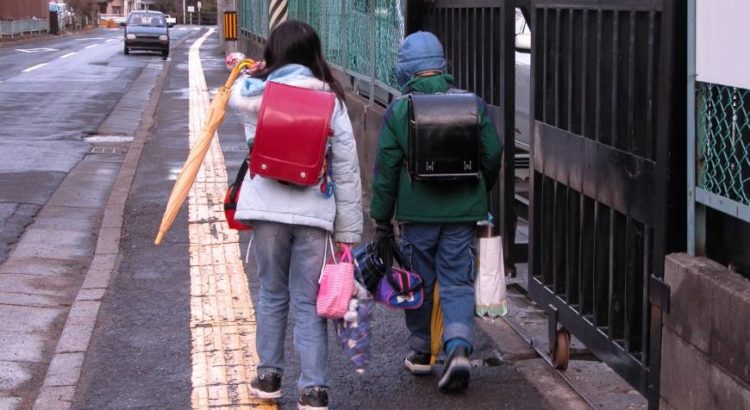
This is ironic, in view of the importance society attaches to education. Arrestingly symbolic, as the back-to-school season nears, is the iconic randoseru elementary school rucksack. The word, borrowed from Dutch, reflects the age and origin of the import, harking back as it does to the early 19th century, when a restricted number of Dutch traders were almost the only foreigners permitted in Japan. They bequeathed to their hosts a few European books, a smattering of the Dutch language, a bit of European science (and a hunger for more) — and the randoseru. Japanese kids have been saddled with it ever since.
It’s no light burden. And it’s gaining weight, as the Asahi Shimbun noted last week. Carrying a full load of books, lunch, gym clothes and whatnot, it can weigh nearly 10 kilograms. The 7-year-old second-grader gamely bracing against its downward thrust probably weighs little more than 20 kg him- or herself.
Why should the venerable randoseru be gaining weight? Because, the Asahi explains, textbooks are. There’s so much to learn! Never more than now, and more and more each year as knowledge, competition, pressure and standards rise. As of 2015, after six years of elementary schooling, an average child will have carried (and hopefully read) a total of 6,518 textbook pages — representing a 34 percent increase in 10 years. Moral education, a new subject swelling the curriculum beginning this year, will add, over six years, an estimated 1,067 pages to the load.
“Higher” education, meanwhile, languishes. “Higher education” used to mean, simply, college. A hundred years ago less than half the population got beyond elementary school, which alone was compulsory. College was for the lucky and gifted few.
Postwar democracy flung open the academic gates. What had been a mark of distinction became more or less a necessity to anyone with white-collar aspirations. Today, “higher education” means — if it means anything — not university education per se but learning for its own sake, and Shukan Gendai’s coverage is not encouraging.
It shows the number of Ph.D. students declining at a rate the declining student-age population only partly accounts for: 14,927 nationwide in 2016 as against 18,232 in 2003.
Philosophy remains a popular university alternative to raw science. Each year brings forth 1,000-odd newly fledged philosophers. They can’t all be professors. Most will have to leave academia and seek their fortunes in the “real world.” As what? Doing what? In an age of post-truth and artificial intelligence, who needs philosophers?
*Michael Hoffman is the author of “In the Land of the Kami: A Journey into the Hearts of Japan” and “Other Worlds.”
Source:
https://www.japantimes.co.jp/news/2018/03/31/national/media-national/much-education-bad-future/#.WsMQOYjwbIU







 Users Today : 68
Users Today : 68 Total Users : 35460199
Total Users : 35460199 Views Today : 97
Views Today : 97 Total views : 3418880
Total views : 3418880