12 DE ABRIL DE 2016 / TRUTH-OUT.ORG/Por: Por Martha Rosenberg y Ronnie Cummins , Organic Consumers Association | Análisis de noticias
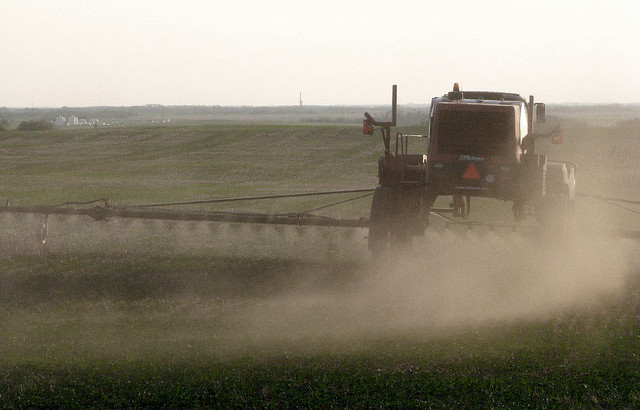
Resumen: ¿Qué sabe usted acerca de la industria de los fertilizantes químicos en todo el mundo? Si usted es como la mayoría de la gente, no mucho. Hay un montón de cobertura de la prensa y de sensibilización de los consumidores cuando se trata de alimentos y cultivos genéticamente modificados, y los riesgos ambientales de los plaguicidas y medicamentos para animales, pero de la industria de los fertilizantes, no tanto, a pesar de ser el mayor segmento de la agroindustria corporativa con al menos 175 $ millones de dólares en ventas anuales, y la mayor fuerza destructiva de contaminar el medio ambiente, lo que altera el clima y la salud pública. Aprender los hechos sobre los fertilizantes químicos y las empresas que los producen le dará una razón más para boicotear los alimentos químicos, granjas industriales y elegir los productos orgánicos de origen animal. Según las normas orgánicas establecidas por el Departamento de Agricultura de Estados Unidos (USDA) se prohíben el uso de fertilizantes químicos, pesticidas, transgénicos, o medicamentos para animales. En esta noticia se plantean cuestiones ambientales y regulatorios inquietantes sobre la transnacional de Monsanto: 1.) es la industria más grande de fertilizantes químicos y agroalimentaria mundial; 2.) Fracking ha alcanzado para los EE.UU. un enorme Productor nitrógeno de fertilizantes; 3.) Koch Industries es un líder de Fertilizantes; 4.) de fertilizantes químicos «Aplicación» es a menudo el autocontrol de la Agencia de Protección Ambiental (EPA); 5.) El nitrógeno de fertilizantes contamina el medio ambiente y el agua potable; 6.) Fertilizantes nitrogenados trabajadores daño y comunidades; 7.) Los fertilizantes químicos destruir la capacidad natural de los suelos para secuestrar el exceso de CO2 atmosférico; 8.) Las emisiones de óxido nitroso de los fertilizantes químicos son una gran contaminante y gases de efecto invernadero persistente. La situación es grave cuando entendemos que dos tercios del suministro de agua potable de Estados Unidos están contaminados con altos niveles de nitratos o nitritos cancerígenos, casi todos de uso excesivo de fertilizantes nitrogenados sintéticos. Algunos pozos públicos tienen nitrógeno a un nivel tan alto que es peligroso e incluso mortal para los niños beban agua del grifo. El fertilizante de nitrógeno es también el mayor contribuyente a las famosas «zonas muertas» en el Golfo de México, la Bahía de Chesapeake, las costas de California y Oregon, y otros 400 lugares en todo el mundo. Dado que se utilizó muy poco de fertilizante de nitrógeno sintético antes de 1950, todos los daños que vemos se produjo hoy en día en los últimos 60 años. Nitratos excesivas de agua, común en las zonas productoras de maíz de los EE.UU. potable, se sabe que causan mortal «bebé azul «síndrome en los bebés, y se han relacionado con el cáncer en adultos. En combinación con los residuos de herbicidas como la atrazina de Syngenta, nitratos se vuelven aún más tóxico , que puede causar daño cerebral y trastornos hormonales.
Artículo original:
There’s plenty of press coverage and consumer awareness when it comes to genetically engineered food and crops, and the environmental hazards of pesticides and animal drugs. But the fertilizer industry? Not so much — even though it’s the largest segment of corporate agribusiness, and a major destructive force in disrupting the climate and damaging public health.
What do you know about the worldwide chemical fertilizer industry? If you’re like most people, not much.
There’s plenty of press coverage and consumer awareness when it comes to genetically engineered food and crops, and the environmental hazards of pesticides and animal drugs. But the fertilizer industry? Not so much — even though it’s the largest segment of corporate agribusiness ($175 billion in annual sales), and a major destructive force in polluting the environment, disrupting the climate, and damaging public health.
Learning the facts about chemical fertilizers and the companies who produce them will give you yet another reason to boycott chemical/GMO/factory farmed foods and choose organic and grassfed animal products instead. Remember, organic standards established by the US Department of Agriculture (USDA) prohibit the use of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, GMOs, or animal drugs.
Here’s a list of underreported facts that raise disturbing environmental and regulatory questions about Monsanto’s Evil Twin — the chemical fertilizer industry. 1.) Chemical Fertilizer Is the Largest Industry in Global Agribusiness According to the ETC group, a watchdog organization that researches the socioeconomic and ecological impacts of industrial agriculture and GMOs, the world’s seven dominant pesticide, GM, and seed companies (including Monsanto, DuPont, Dow, Bayer, and Syngenta) represent a $93 billion market. The global, energy-intensive chemical fertilizer industry is almost twice as large, at $175 billion.
Like most of the other multinational players in Big Food Inc., the fertilizer industry has secretive, vertical or «cartel» like qualities that obscure operations and make regulation difficult. Increasingly, seed and GMO companies, farm equipment producers, pesticide/herbicide makers and crop and soil data producers work in each others’ interest seamlessly and behind the scenes, according to ETC.
As ETC points out: «With combined annual revenue of over $385 billion, these companies call the shots. Who will dominate the industrial food chain? And what does it mean for farmers, food sovereignty and climate chaos?» Industrially mined phosphorus and potash, along with synthetic nitrogen, are major components of the fertilizer industry. Up to 85 percent of the world’s known phosphate rock reserves are located in Morocco. About 70 percent of potash comes from former Soviet states and Canada. 2.) Fracking Has Made the US a Huge Nitrogen Fertilizer Producer In recent years, US production of nitrogen fertilizer has boomed thanks to the falling price of natural gas used in its production. The reason for the cheap gas of course is fracking — the process of extracting gas from rock formations by bombarding them with pressurized water spiked with toxic chemicals. Unfortunately, fracking releases large amounts of climate disrupting methane and toxic chemical laden fracking liquids which can permanently pollute underground aquifers.
That’s bad for the environment — but good for fertilizer companies. Thanks to low natural gas prices, after decades of importing nitrogen fertilizer from the Middle East, the number of US nitrogen fertilizer plants is growing. The three leading domestic producers — Koch Industries, Orascom Construction Industries and CF Industries — are reaping the benefits. Who’s driving demand for all this nitrogen fertilizer? Monsanto.
Between 2005 and 2010, US growers of genetically engineered corn, largely for GMO animal feed and ethanol, increased their nitrogen fertilizer use by one billion pounds. New nitrogen fertilizer plants are being situated close to the corn and soybean growers to feed demand more efficiently. «It is a highly concentrated and oligopolistic-type industry,» says Glen Buckley, a fertilizer industry consultant who spent 30 years working at CF Industries, based in Deerfield, Ill. 3.) Koch Industries Is a Fertilizer Leader In 2010, Koch Industries was named «the world’s third-largest maker and marketer of nitrogen fertilizer,» according to the Wichita Eagle. Koch, which along with Monsanto is one of the most hated corporations in the US, is infamous for its support of extreme right-wing politicians and climate deniers. Koch Industries is part of a large system «of buying, leasing, upgrading and expanding fertilizer manufacturing, trading and distribution facilities worldwide.» It controls over 65 terminals «where it wholesales nitrogen fertilizer to co-ops and grain elevators for sale to farmers, as well as selling to the chemical industry,» reported the Eagle. Not surprisingly, Koch’s fertilizer unit, called Koch Agronomics, has drawn the ire of environmentalists. Pollution is «strictly monitored and legally permitted by federal, state and local governments,» Steve Packebush, president of Koch Fertilizer and vice president for nitrogen for Koch Industries told the Eagle. But how strict are those guidelines, really? 4.) Chemical Fertilizer «Enforcement» Is Often Self-Monitoring The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) acknowledges the severe harm nitrogen fertilizer does to waterways, including to marine life and humans. Yet the agency’s «enforcement» of harmful excessive farm runoff sounds a lot like an honor system.
Asked how National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) permits, which allow farming operations to discharge nitrogen, are «enforced,» the EPA says, «The permit will require the facility to sample its discharges and notify EPA and the state regulatory agency of these results. In addition, the permit will require the facility to notify EPA and the state regulatory agency when the facility determines it is not in compliance with the requirements of a permit. EPA and state regulatory agencies also will send inspectors to companies in order to determine if they are in compliance with the conditions imposed under their permits.» Self-monitoring by private industry is of course a government trend across the board. In the late 1990’s the government rolled out the Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) program which took away the majority of those «pesky» federal meat inspectors’ duties and allowed Big Meat to self-police its own slaughterhouses. Sometimes US meat inspectors were openly defied and laughed at. HACCP was quickly dubbed Have a Cup of Coffee and Pray. Meat inspectors identified greater amounts of feces and contamination in meat soon after the program was instituted. Since then, self-policing by food producers has only been expanded. 5.) Nitrogen Fertilizer Pollutes the Environment and Drinking Water As most people know, nitrogen runoff from non-organic farms and feedlots into waterways causes hypoxic conditions — lack of oxygen — which regularly kill fish in shocking quantities.
Two-thirds of the US drinking water supply is contaminated at high levels with carcinogenic nitrates or nitrites, almost all from excessive use of synthetic nitrogen fertilizer. Some public wells have nitrogen at such a high level that it is dangerous and even deadly for children to drink the tap water.
Nitrogen fertilizer is also the greatest contributor to the infamous «dead zones» in the Gulf of Mexico, the Chesapeake Bay, the coasts of California and Oregon, and 400 other spots around the world. Since very little synthetic nitrogen fertilizer was used before 1950, all of the damage we see today occurred in the last 60 years. Excessive nitrates in drinking water, common in the corn-growing areas of the US, are known to cause deadly «blue baby» syndrome in infants, and have been linked to cancer in adults. In combination with herbicide residues such as Syngenta’s atrazine, nitrates become even more toxic, potentially causing brain damage and hormone disruption.
In some rural areas, fertilizer pollution levels are 10 times beyond so-called «allowable levels,» although golf courses and homeowner fertilizer and pesticide use in urban areas also contribute to the problem. Last fall, the Des Moines Water Works sued three neighboring farming counties over their nitrate discharges but, reported the Associated Press, «the litigation has provoked intense criticism from Iowa’s powerful agricultural industry, which argues that farmers are already taking voluntary measures to control them.» 6.) Nitrogen Fertilizers Harm Workers and Communities Anhydrous ammonia, a nitrogen compound compressed into a clear, colorless liquid for easy application, is extremely dangerous to workers and neighboring communities. It poses explosion and fire hazards as well as respiratory risks.
«It [Anhydrous ammonia] must be stored and handled under high pressure, requiring specially designed and well-maintained equipment,» says the University of Minnesota’s extension site. «In addition, to ensure their safety, workers must be adequately educated about the procedures and personal protective equipment required to safely handle this product.» In 2013, an anhydrous ammonia explosion and fire at the West Fertilizer Company storage near Waco, Texas, killed 15 and injured 160, and caused 150 buildings to be razed. (At the time, Governor Rick Perry was in Chicago recruiting businesses to relocate in Texas, where safety regulations were more lax and would not cut into their profits.) In 2006, railroads asked to be relieved of their common carrier obligation to haul fertilizer products like anhydrous ammonia or to be protected by a liability cap. Accidents like last year’s in South Carolina, where people within a 1.5- mile radius of a derailed train carrying ammonium nitrate and anhydrous ammonium were evacuated, occur regularly. Yet the Fertilizer Institute trade group says «The historically high safety record of anhydrous ammonia transport by rail has been achieved over the years by the fertilizer industry, the railroads and tank car manufacturing and leasing companies working in a close cooperative effort.»
7.) Chemical Fertilizers Destroy the Soils’ Natural Ability to Sequester Excess Atmospheric CO2 According to GMO no-till advocates, adding nitrogen fertilizer to soil, is supposedly «climate friendly» because it allegedly helps crops draw CO2 from the atmosphere and sequester it in the soil as organic carbon. But University of Illinois soil scientists disputed this view in «The Myth of Nitrogen Fertilization for Soil Carbon Sequestration,» a research paper published in the Journal of Environmental Quality:
«…excessive [fertilizer] application rates cut profits and are bad for soils and the environment. The loss of soil carbon has many adverse consequences for productivity, one of which is to decrease water storage. There are also adverse implications for air and water quality, since carbon dioxide will be released into the air, while excessive nitrogen contributes to the nitrate pollution problem.»
Not surprisingly, much of the organic carbon decline the researchers identified occurred in the fertilized soil found in corn belts. The ETC group agrees with the University of Illinois researchers.
There is growing recognition that synthetic fertilizers are a major contributor to climate-destroying greenhouse gases (GHG). The estimated cost of environmental damage from reactive nitrogen emissions is between $70 billion and $320 billion in the European Union alone.»
8.) Nitrous Oxide Emissions From Chemical Fertilizers Are a Major and Persistent Greenhouse Gas Pollutant
Nitrous oxide (N2O) is responsible for approximate 5 percent of all US greenhouse gas emissions from human activities. Nitrous oxide is naturally present in the atmosphere as part of the Earth’s nitrogen cycle, and has a variety of natural sources. However, human activities such as agriculture, fossil fuel combustion, wastewater management, and industrial processes are increasing the amount of N2O in the atmosphere.
The primary cause of N2O contamination of the atmosphere are the nitrogen fertilizers used in industrial (non-organic) agriculture.
Nitrous oxide molecules, in comparison to other greenhouse gases such as CO2 and methane, stay in the atmosphere for a very long time, an average of 114 years. NO2 also has much more potent heat-trapping characteristics. The impact of one pound of N2O on warming the atmosphere is 300 times that of one pound of carbon dioxide.
Although transportation, industry and energy producers are significant and well-recognized GHG polluters, few people understand that the worst US greenhouse gas emitter is «Food Incorporated,» industrial food and farming. Industrial food and farming accounts for a huge portion of US greenhouse gas emissions. EPA’s ridiculously low estimates range from 7 percent to 12 percent, but some climate scientists believe the figure could be as high as 50 percent or more. Industrial food and farming also destroys the natural capacity of plants and soils to sequester atmospheric carbon.
Many climate scientists now admit that they have previously drastically underestimated the dangers of the non-CO2 GHGs, including nitrous oxide, which are responsible (along with methane) for at least 20 percent of global warming.
Nearly all nitrous oxide pollution comes from dumping billions of pounds of synthetic nitrogen fertilizer and sewage sludge on farmland (chemical fertilizers and sludge are banned on organic farms and ranches), mainly to grow animal feed or produce ethanol. Given that about 80 percent of US agriculture is devoted to producing factory-farmed meat, dairy and animal feed, reducing agriculture GHGs means eliminating the over-production and over-consumption of factory-farmed meat and animal products.
The most climate-damaging greenhouse gas poison used by industrial farmers is synthetic nitrogen fertilizer. Pesticide manufacture and use are also serious problems, which generate their own large share of GHGs during manufacture and use (more than 25 billion pounds per year). But, about six times more chemical fertilizer is used than toxic pesticides on US farms.
German chemical corporations developed the industrial processes for the two most widely used forms of synthetic nitrogen in the early 1900s. But until World War II, US use of synthetic nitrogen as a fertilizer was limited to about 5 percent of the total nitrogen applied. Up until that time most nitrogen inputs came from animal manures, composts and fertilizer (cover) crops, just as it does on organic farms today.
During the Second World War, all of the European powers and the US greatly expanded their facilities for producing nitrogen for bombs, ammunition and fertilizer for the war effort. Since then, both the use of nitrogen fertilizer and bomb-making capacity have soared. By the 1990s, more than 90 percent of nitrogen fertilizer used in the US was synthetic.
According to the USDA, the average US nitrogen fertilizer use per year from 1998 to 2007 was 24 billion 661 million pounds. To produce that nitrogen, the manufacturers released at least 6.7 pounds of GHG for every pound produced. That’s 165 billion, 228 million pounds of GHGs spewed into the atmosphere every year, just for the manufacture of synthetic nitrogen fertilizer. Most of those emissions are nitrous oxide, the most damaging emissions of US agriculture.
Regenerative Organic Farming and Ranching Can Drastically Reduce GHG Emissions
The currently catastrophic, but largely unrecognized, greenhouse gas damage from chemical farms and industrial food production and distribution must be reversed. This will require wholesale changes in farming practices, government subsidies, food processing and handling. It will require the conversion of millions of chemical farms, feedlots and CAFOs (concentrated animal feeding operations) to organic production. It will require the establishment of millions of urban backyard and community gardens. If we carried out a full environmental impact statement on industrial and factory farming synthetic nitrogen fertilizer use, we would never give these practices a permit for agricultural use. Ironically, although factory farming is responsible for more GHGs than any other US industry, it will not be regulated under proposed EPA regulations designed to limit GHGs, unless citizens demand it. We must demand that methane pollution from factory farms and synthetic nitrogen fertilizer pollution on chemical farms be highly taxed and regulated in the short term, and phased out, as soon as possible. We must substitute instead cover crops, compost and compost tea, as currently utilized in organic farming and ranching.
In the meantime, consumers should boycott all foods and products emanating from Monsanto and its Evil Twin: the chemical fertilizer industry.
Fuente: http://www.truth-out.org/news/item/35575-monsanto-s-evil-twin-disturbing-facts-about-the-fertilizer-industry



















 Users Today : 29
Users Today : 29 Total Users : 35460160
Total Users : 35460160 Views Today : 43
Views Today : 43 Total views : 3418826
Total views : 3418826