EE.UU./02 de septiembre de 2016/news.harvard.edu
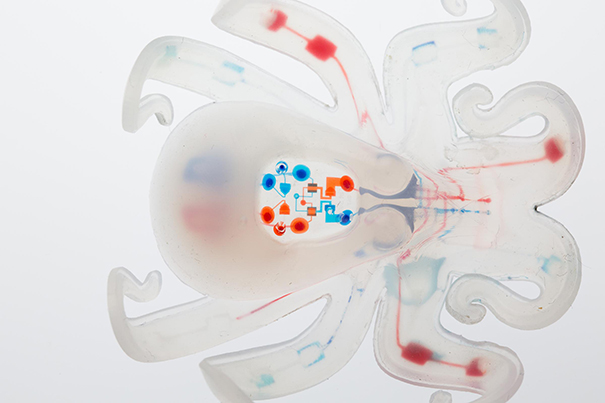
Resumen: Desarrollado por una reacción química controlada por la microfluídica. Un equipo de investigadores de la Universidad de Harvard con experiencia en la impresión 3-D, ingeniería mecánica, y microfluídica ha demostrado el primer robot autónomo sin ataduras, totalmente suave. Este pequeño robot impresa-3-D – apodado el «octobot» – podría allanar el camino para una nueva generación de este tipo de máquinas. La robótica suave puedan ayudar a revolucionar cómo los seres humanos interactúan con las máquinas. Pero los investigadores han tenido dificultades para construir robots totalmente compatibles con sistemas eléctricos de potencia y control – como las baterías y placas de circuito – son rígidos, y hasta ahora los robots de cuerpo blando han sido o bien atados a un sistema off-board o aparejado con componentes duros. «Las fuentes de combustible para robots blandos siempre han confiado en algún tipo de componentes rígidos», dijo Michael Wehner, un becario postdoctoral en el laboratorio de madera y co-primer autor del artículo. «Lo maravilloso de peróxido de hidrógeno es que una simple reacción química entre el y un catalizador – en este caso, el platino – nos permite sustituir las fuentes de poder rígidas.» Para controlar la reacción, el equipo utilizó un circuito lógico de microfluidos basada en el trabajo pionero de co-autor y el químico George Whitesides, el Woodford L. y profesor de la Universidad Ann A. Flores y un miembro de la facultad núcleo de la Wyss. El circuito, un análogo suave de un simple oscilador electrónico, controla cuando el peróxido de hidrógeno se descompone en gas en el octobot. «Todo el sistema es simple de fabricar. Mediante la combinación de tres métodos de fabricación – la litografía blanda, piezas de fundición, y la impresión 3-D.
Noticia Original:
Ateam of Harvard University researchers with expertise in 3-D printing, mechanical engineering, and microfluidics has demonstrated the first autonomous, untethered, entirely soft robot. This small, 3-D-printed robot — nicknamed the “octobot” — could pave the way for a new generation of such machines.
Soft robotics could help revolutionize how humans interact with machines. But researchers have struggled to build entirely compliant robots. Electric power and control systems — such as batteries and circuit boards — are rigid, and until now soft-bodied robots have been either tethered to an off-board system or rigged with hard components.
“One longstanding vision for the field of soft robotics has been to create robots that are entirely soft, but the struggle has always been in replacing rigid components like batteries and electronic controls with analogous soft systems and then putting it all together,” said Wood. “This research demonstrates that we can easily manufacture the key components of a simple, entirely soft robot, which lays the foundation for more complex designs.”
“Through our hybrid assembly approach, we were able to 3-D print each of the functional components required within the soft robot body, including the fuel storage, power, and actuation, in a rapid manner,” said Lewis. “The octobot is a simple embodiment designed to demonstrate our integrated design and additive fabrication strategy for embedding autonomous functionality.”
Octopuses have long been a source of inspiration in soft robotics. These curious creatures can perform incredible feats of strength and dexterity with no internal skeleton.
Harvard’s octobot is pneumatic-based, and so is powered by gas under pressure. A reaction inside the bot transforms a small amount of liquid fuel (hydrogen peroxide) into a large amount of gas, which flows into the octobot’s arms and inflates them like balloons.
“Fuel sources for soft robots have always relied on some type of rigid components,” said Michael Wehner, a postdoctoral fellow in the Wood lab and co-first author of the paper. “The wonderful thing about hydrogen peroxide is that a simple reaction between the chemical and a catalyst — in this case platinum — allows us to replace rigid power sources.”
To control the reaction, the team used a microfluidic logic circuit based on pioneering work by co-author and chemist George Whitesides, the Woodford L. and Ann A. Flowers University Professor and a core faculty member of the Wyss. The circuit, a soft analog of a simple electronic oscillator, controls when hydrogen peroxide decomposes to gas in the octobot.
Powering the Octobot: A chemical reaction
“The entire system is simple to fabricate. By combining three fabrication methods — soft lithography, molding, and 3-D printing — we can quickly manufacture these devices,” said Ryan Truby, a graduate student in the Lewis lab and co-first author of the paper.
The simplicity of the assembly process paves the way for designs of greater complexity. Next, the Harvard team hopes to design an octobot that can crawl, swim, and interact with its environment.
“This research is a proof of concept,” Truby said. “We hope that our approach for creating autonomous soft robots inspires roboticists, material scientists, and researchers focused on advanced manufacturing.”
The paper was co-authored by Daniel Fitzgerald of the Wyss Institute and Bobak Mosadegh of Cornell University. The research was supported by the National Science Foundation through the Materials Research Science and Engineering Center at Harvard and by the Wyss Institute.
Tomado de: http://news.harvard.edu/gazette/story/2016/08/the-first-autonomous-entirely-soft-robot/





 Users Today : 59
Users Today : 59 Total Users : 35459965
Total Users : 35459965 Views Today : 74
Views Today : 74 Total views : 3418539
Total views : 3418539